su Linux Command
Overview
The su command is substitute user in Linux. The command is used to switch to a particular user and it needs the password of the user that we are trying to switch.
$ su <user account>
Example
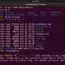
When the command is called without arguments, it defaults to the root user. For example, if we want to switch to john user account.
$ su – john
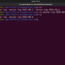
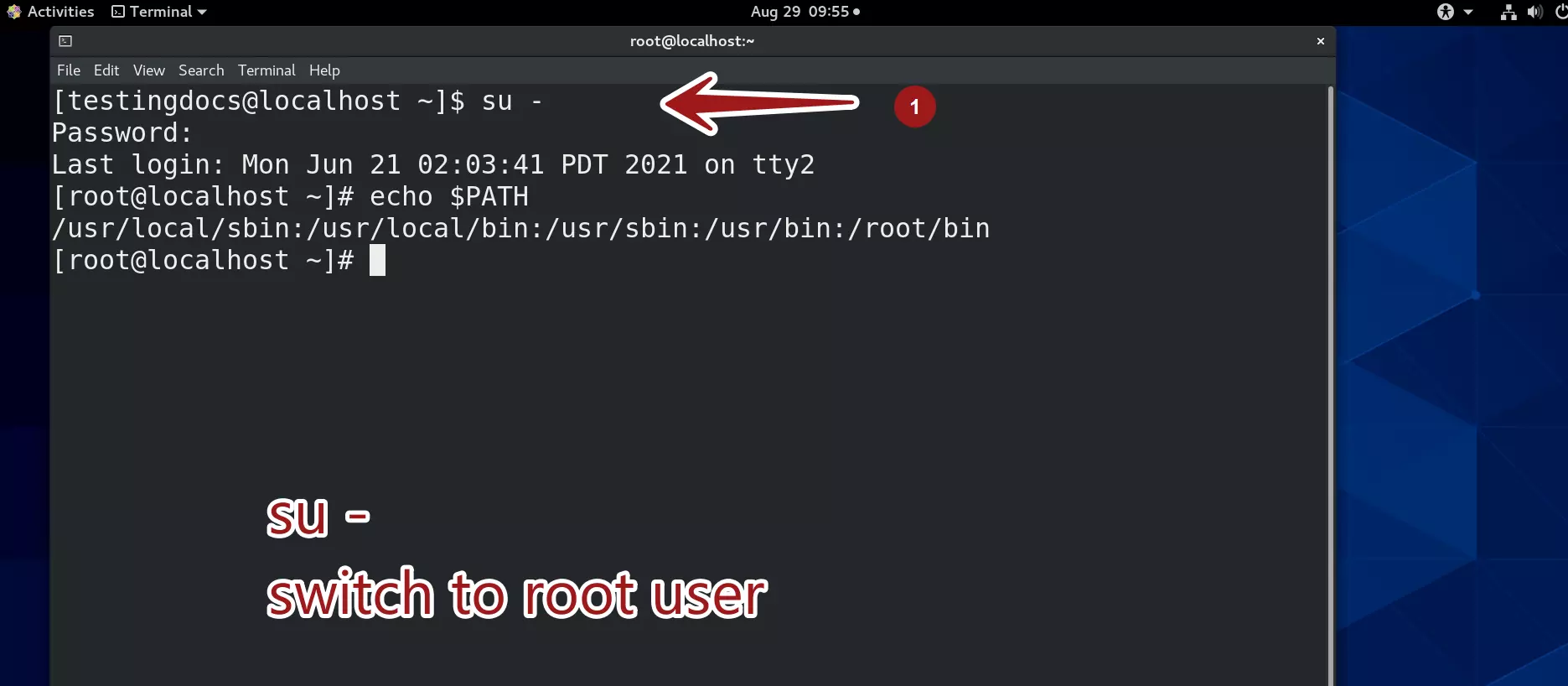
The (-) switch allows to include john’s environment variables and the path during the switch. So, to switch to root user with root’s environment we can use:
$ su –
–
Linux Basic Commands Tutorial page:
https://www.testingdocs.com/linux-basic-commands-tutorial/
More Information on Ubuntu Linux:
https://ubuntu.com/