Teletype Network Protocol (Telnet)
Telnet Protocol
Teletype Network Protocol (in short, Telnet) is a protocol for remotely accessing computers or devices over a computer network. It allows a user to establish a Command-Line Interface (CLI) session with a remote device, such as a server, router, or switch, and execute commands on that device as if they were physically at the console.
The Telnet protocol establishes a virtual terminal connection between the local computer and the remote device. The user enters Telnet commands into their local terminal, which are transmitted over the network to the remote device. The remote device then executes those commands and sends the output back to the user’s terminal, where it is displayed.
Telnet Port
Telnet is a network protocol that provides bidirectional interactive communication between two devices over a network. The default port number for the Telnet protocol is 23.
When a Telnet client connects to a Telnet server, it establishes a TCP connection with the server on port 23. This connection exchanges text-based data between the client and the server. Telnet is an unencrypted protocol, meaning all data transmitted between the client and the server is sent in clear text and can potentially be intercepted by third parties.
How to enable Telnet
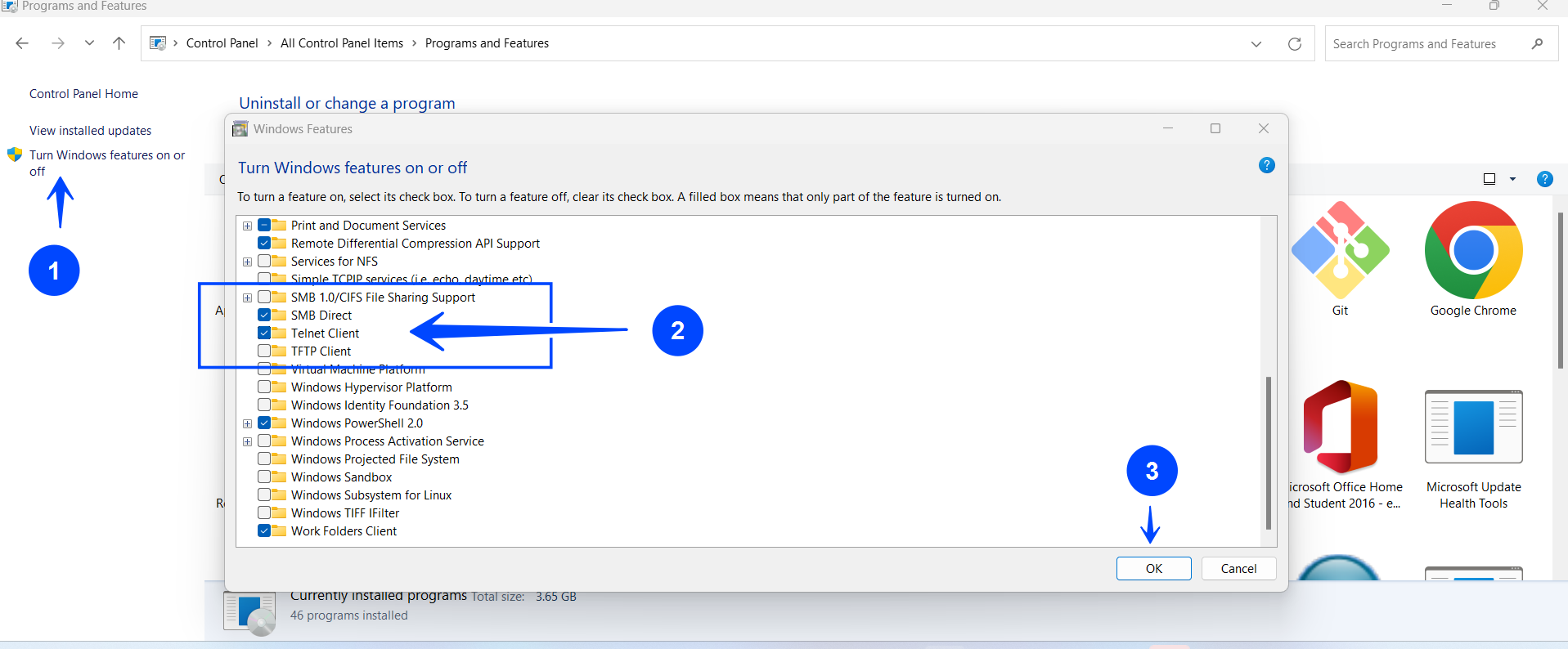
Telnet is not enabled by default on Windows because it is considered a security risk. However, if you need to use Telnet, you can enable it by following these steps:
- Open the Control Panel.
- Click on Programs and Features.
- Click on Turn Windows features on or off.
- Scroll down and find Telnet Client in the list.
- Check the box next to Telnet Client to enable it.
- Click OK to save the changes.
Wait for Windows to install the Telnet client.
Once the Telnet client is enabled, you can use it by opening a command prompt and typing “telnet” followed by the IP address or hostname of the device you want to connect to.
For example, if you want to connect to a device with the IP address 192.168.1.1, you would type “telnet 192.168.1.1” at the command prompt.
Telnet has been widely used in the past for remote administration and management of devices, but its use has decreased in recent years due to security concerns. Telnet sends all data, including login credentials, in plaintext over the network, which makes it vulnerable to interception and eavesdropping.
Telnet has largely been replaced by more secure protocols such as SSH (Secure Shell). SSH (Secure Shell) encrypts data transmission, making it less susceptible to interception or eavesdropping.
—
Windows 11 Tutorials
https://www.testingdocs.com/windows-11-tutorials/
More Information on Windows 11