Types of JDBC Drivers
Overview
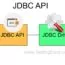
JDBC drivers are available from a number of vendors. The drivers support different versions of the JDBC API. JDBC driver might be written purely in Java or in a mixture of the Java and Java native (JNI) methods.
There are basic four types of JDBC Drivers. They are categorized as follows:
- Type 1 – JDBC-ODBC Bridge Driver
- Type 2 – Native API partly Java Driver
- Type 3 – Middleware Driver
- Type 4 – Pure Java Driver
Type 1
Type 1 drivers implement the JDBC API as a mapping to another data access API. The JDBC-ODBC (Open Data Base Connectivity) Bridge driver is an example of this driver. Type 1 drivers are dependent on the native library, so they are not portable to other machine architectures.
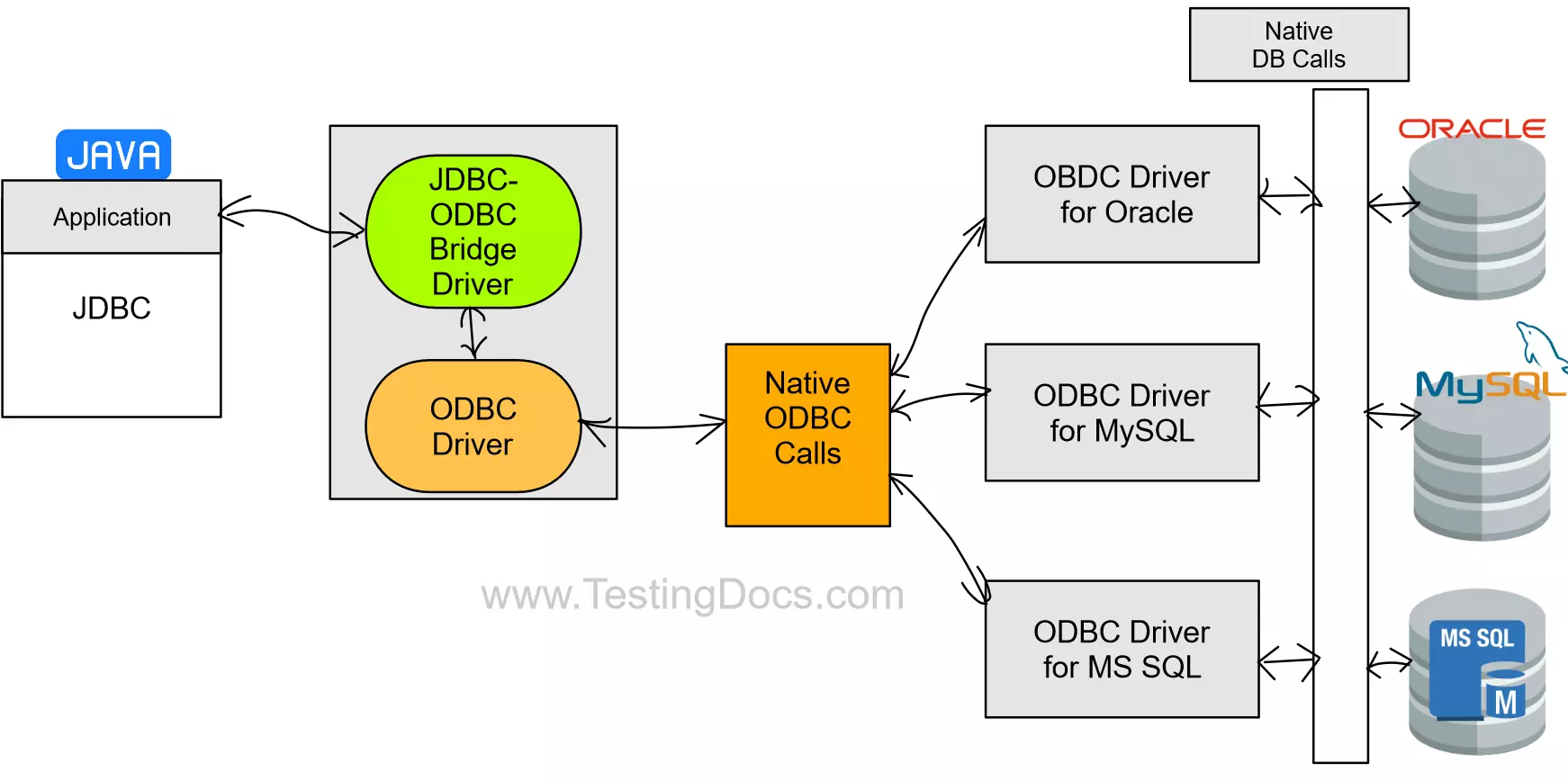
Type 2
Type 2 drivers are written partly in Java and partly in native API. They use a native client library specific to the data source to which they connect.
Type 3
Type 3 drivers use a pure Java client and communicate through the network using a database-independent protocol with the middleware. The middleware server then communicates the JDBC client’s requests to the data source.
Type 4
Type 4 drivers are pure 100% Java and implement the network protocol for a specific data source. The JDBC client connects directly to the data source. These drivers are platform-independent and can be used in Java applications.
Example:
Oracle JDBC Thin Driver is a Type 4 driver that can be client-side or server-side and is stateful.
—
Java Tutorials
Java Tutorial on this website:
https://www.testingdocs.com/java-tutorial/
More information about Oracle Database: