Understanding a Simple C Program
Introduction
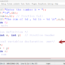
In this post, we will understand a simple C program to add two numbers and display the output of the sum. C program shown below:
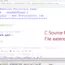
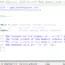
#include<stdio.h>
/* Program to calculate
* sum of Two numbers a,b
*/
int main()
{
int a = 15; // Initialize a to 15.
int b = 25; // Initialize b to 25.
int sum = 0; // Initialize sum to 0.
sum = a + b;
printf("Sum is:%d", sum);
return 0;
}
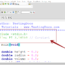
Preprocessor directive:
#include<stdio.h> The #include statement is called a preprocessor directive. A preprocessor directive begins with a # sign. These statements are processed before compilation. The above directive tells the preprocessor to include the “stdio.h” header file to support standard I/O operations. 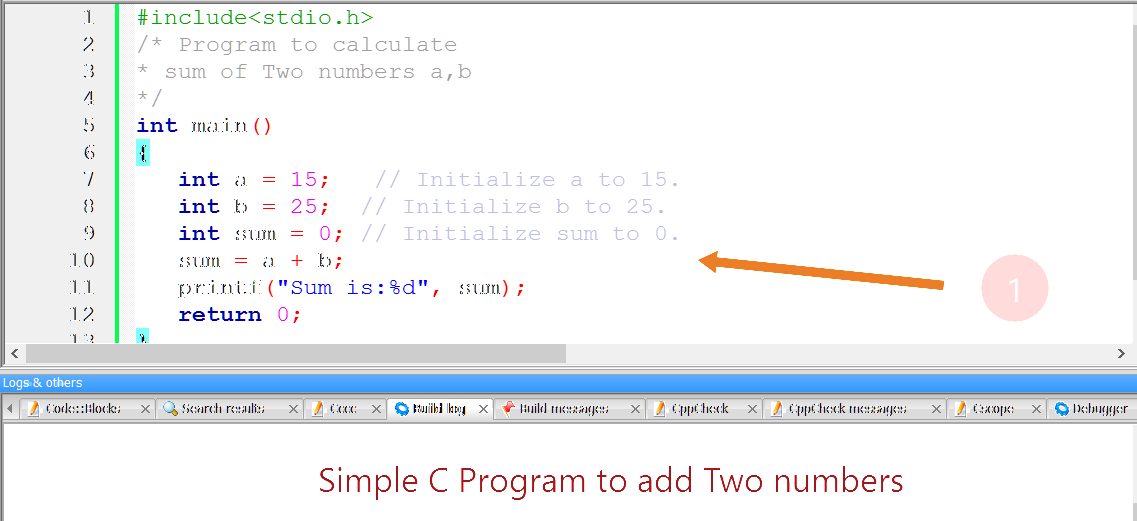
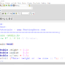
Comments:
Comments are not executable statements. They are ignored by the compiler. Comments usually provide useful explanation and documentation of your programs to others. There are two kinds of comments:
/* Program to calculate
* sum of Two numbers a,b
*/
Multi-line Comment begins with /* and ends with */. It may span more than one lines
// Initialize a to 15.
Single line comments begins with // and lasts until the end of the current line
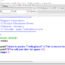
main()
int main() {
…
}
The main() function is the entry point of program execution. main() is required to return an int (integer). Declaring variables a,b and sum. For example we have declared integer a to hold 15 using the below statement. int a = 15; Assigning the sum of two numbers a and b to sum variable.
sum = a + b;
printf(“…”);
printf() function is used to print sum on to the console.
printf(“Sum is:%d”, sum);
return 0;
This line is optional.C compiler will implicitly insert a “return 0;” to the end of the main() function. This statement terminates the main() function and returns a value of 0 to the operating system. Typically, return value of 0 signals normal termination; whereas value of non-zero signals abnormal termination.
The IDE used in the tutorial is Code:: Blocks. To download and install Code Blocks follow the link:
https://www.testingdocs.com/download-and-install-codeblocks/
For more information on Code Blocks IDE, visit the official website of Code blocks IDE: http://www.codeblocks.org/