Working with Assert in TestNG framework.
Introduction
While writing tests we may want to know that everything is as expected. ( test data, conditions, navigation flows, etc.) We may have checkpoints at some specific points in our tests. TestNG framework has an in-built provision to work with asserts. We use Assert class in TestNG framework to do assertions in tests.
Assert class
Assert class in TestNG is a static only class. It has a lot of static assertion methods mostly with the following natural order.
The order is actualValue, expectedValue [, message].
Methods in TestNG Assert class.
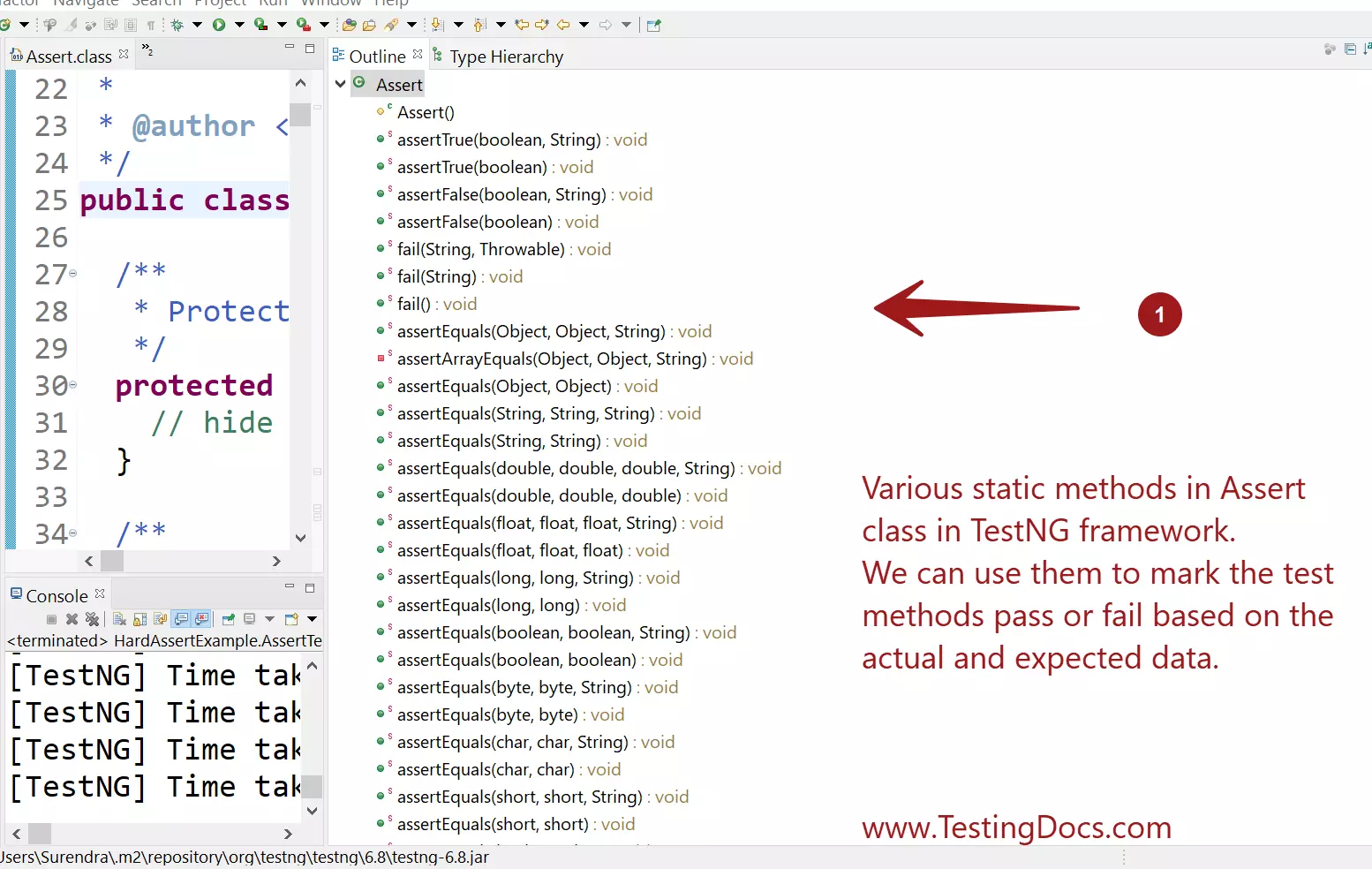
Sample TestNG Assert
package com.testingdocs.selenium.demo;
import org.testng.annotations.Test;
import org.testng.Assert;
public class AssertExample
{
@Test
public void normalAssert()
{
Assert.assertEquals(1, 2, "Assertion One");
}
}
Run output of the test method is as expected a failure with AssertionError.
FAILED: normalAssert java.lang.AssertionError: Assertion One expected [2] but found [1] at org.testng.Assert.fail(Assert.java:94) at org.testng.Assert.failNotEquals(Assert.java:513) at org.testng.Assert.assertEqualsImpl(Assert.java:135) at org.testng.Assert.assertEquals(Assert.java:116) at org.testng.Assert.assertEquals(Assert.java:389) at com.testingdocs.selenium.demo.AssertExample.normalAssert (AssertExample.java:11) at sun.reflect.NativeMethodAccessorImpl.invoke0(Native Method) at sun.reflect.NativeMethodAccessorImpl.invoke(Unknown Source) at sun.reflect.DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl.invoke(Unknown Source) at java.lang.reflect.Method.invoke(Unknown Source) at org.testng.internal.MethodInvocationHelper.invokeMethod (MethodInvocationHelper.java:86) at org.testng.internal.Invoker.invokeMethod(Invoker.java:646) at org.testng.internal.Invoker.invokeTestMethod(Invoker.java:823) at org.testng.internal.Invoker.invokeTestMethods(Invoker.java:1131) at org.testng.internal.TestMethodWorker.invokeTestMethods (TestMethodWorker.java:129) at org.testng.internal.TestMethodWorker.run(TestMethodWorker.java:112) at org.testng.TestRunner.privateRun(TestRunner.java:778) at org.testng.TestRunner.run(TestRunner.java:632) at org.testng.SuiteRunner.runTest(SuiteRunner.java:366) at org.testng.SuiteRunner.runSequentially(SuiteRunner.java:361) at org.testng.SuiteRunner.privateRun(SuiteRunner.java:319) at org.testng.SuiteRunner.run(SuiteRunner.java:268) at org.testng.SuiteRunnerWorker.runSuite(SuiteRunnerWorker.java:52) at org.testng.SuiteRunnerWorker.run(SuiteRunnerWorker.java:86) at org.testng.TestNG.runSuitesSequentially(TestNG.java:1225) at org.testng.TestNG.runSuitesLocally(TestNG.java:1150) at org.testng.TestNG.runSuites(TestNG.java:1075) at org.testng.TestNG.run(TestNG.java:1047) at org.testng.remote.AbstractRemoteTestNG.run(AbstractRemoteTestNG.java:126) at org.testng.remote.RemoteTestNG.initAndRun(RemoteTestNG.java:137) at org.testng.remote.RemoteTestNG.main(RemoteTestNG.java:58) =============================================== Default test Tests run: 1, Failures: 1, Skips: 0 ===============================================
Now, lets add another assertion and see what happens.
package com.testingdocs.selenium.demo;
import org.testng.annotations.Test;
import org.testng.Assert;
public class AssertExample
{
@Test
public void normalAssert()
{
Assert.assertEquals(1, 2, "Assertion One");
Assert.assertEquals(1, 1, "Assertion Two");
}
}
FAILED: normalAssert
java.lang.AssertionError: Assertion One expected [2] but found [1]
We are hard on the assertions and we can notice that the second assertion has never run in the above example. So, when we have more than one assertion in our test, this technique will have our tests fail once the first assertion failure is encountered.
static import
If we use a lot of assets in our test class, we may hate to type every time Assert.assertEquals, then we may perform a static import
package com.testingdocs.selenium.demo;
import org.testng.annotations.Test;
import static org.testng.Assert.assertEquals;
public class AssertExample
{
@Test
public void normalAssert()
{
assertEquals(1, 1, "Assertion One");
assertEquals(1, 2, "Assertion Two");
}
}
Explore other assert methods in the Assert class as we might use them while authoring test cases extensively.
TestNG Tutorials on this website can be found at:
https://www.testingdocs.com/testng-framework-tutorial/
For more details on the TestNG Framework, visit the official website of TestNG at: https://testng.org