Android Debug Bridge( adb )
Android Debug Bridge
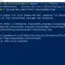
Android Debug Bridge (adb) is a command-line tool for communicating with Android devices. The adb command allows various device actions, such as installing and debugging apps. adb provides access to a command shell for running commands on a device.
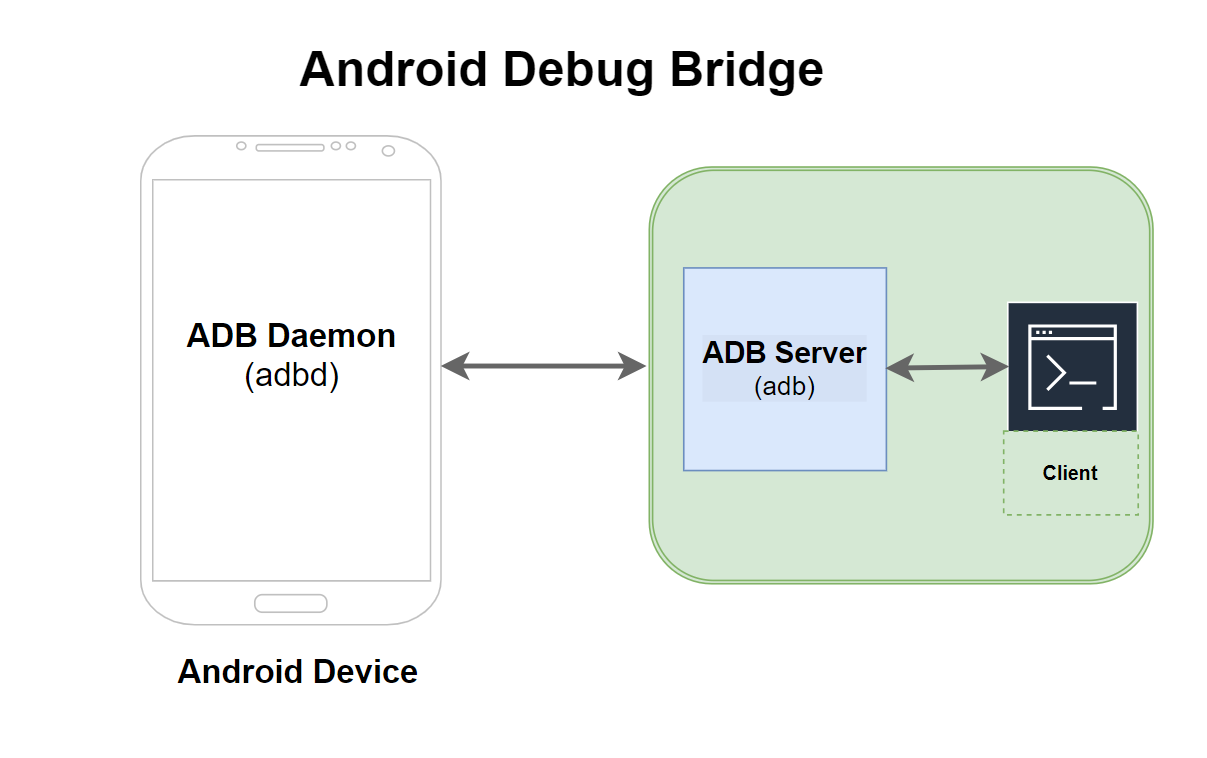
The Android SDK can run the application on the actual Android device or a software emulator on the host machine. The adb is a client-server program and includes three main components.
adb Components
The components are as follows:
- Client
- Daemon
- Server
Client
A client program runs on the developer’s host machine. One can invoke a client from a shell by issuing an adb command. The client is the command line or terminal component that the user interacts with. It is responsible for sending commands to the ADB server. Commands can include installing an app, copying files on the device, etc.
Daemon (adbd)
The daemon program runs as a background process on each Android device (or emulator). It listens for commands from the ADB server and executes them on the device. It is the part that manages communication with the handset or the emulator and helps execute the application.
Server
The server runs on the host machine. It manages the communication between the client and the ADB daemon( on the emulator or the Android handset). It acts as a proxy to relay commands from the client to the daemon and back.
When you execute an adb command, the working process is as follows:
- The client on your machine sends a command to the server.
- The ADB server processes this command and forwards it to the ADB daemon on the connected Android device.
- The ADB daemon executes the command on the device and sends back the response to the server, which then relays it back to the client.
The ADB architecture allows for flexibility and control, enabling developers to perform various actions directly from the development machine on their devices.