cat Linux command
cat Linux command
In this tutorial, we will learn about the cat Linux command with examples. The cat command reads one or more files and prints the file contents to the standard output device, i.e., the computer monitor screen. cat is a short form of “concatenate”. To learn more about the command and the command line switches, type the following command:
$ man cat
Example
#
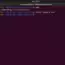
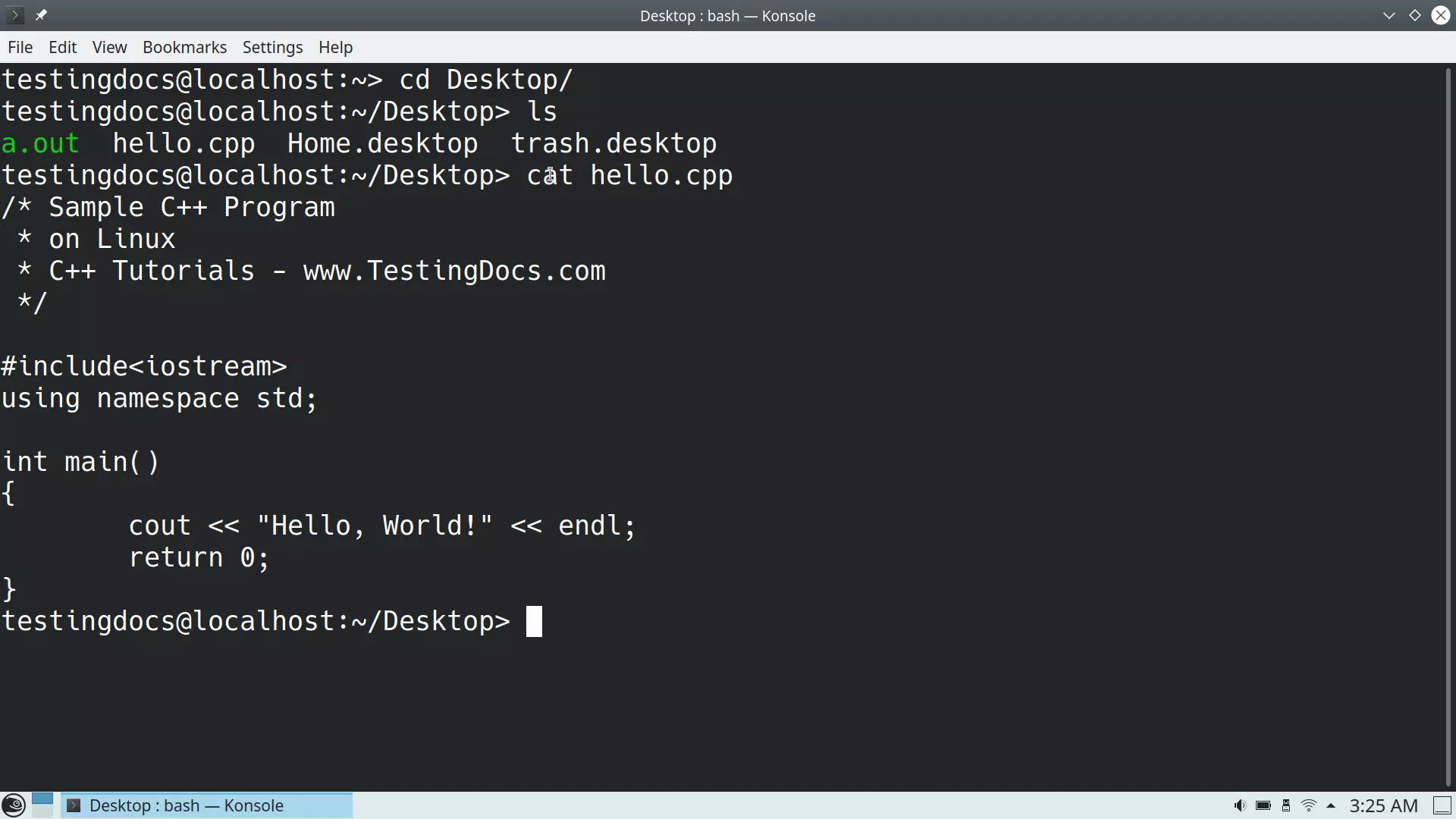
The simple cat command displays the file contents to the screen. For example, to view the file hello.cpp file on the screen.
$ cat hello.cpp
#
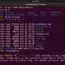
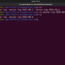
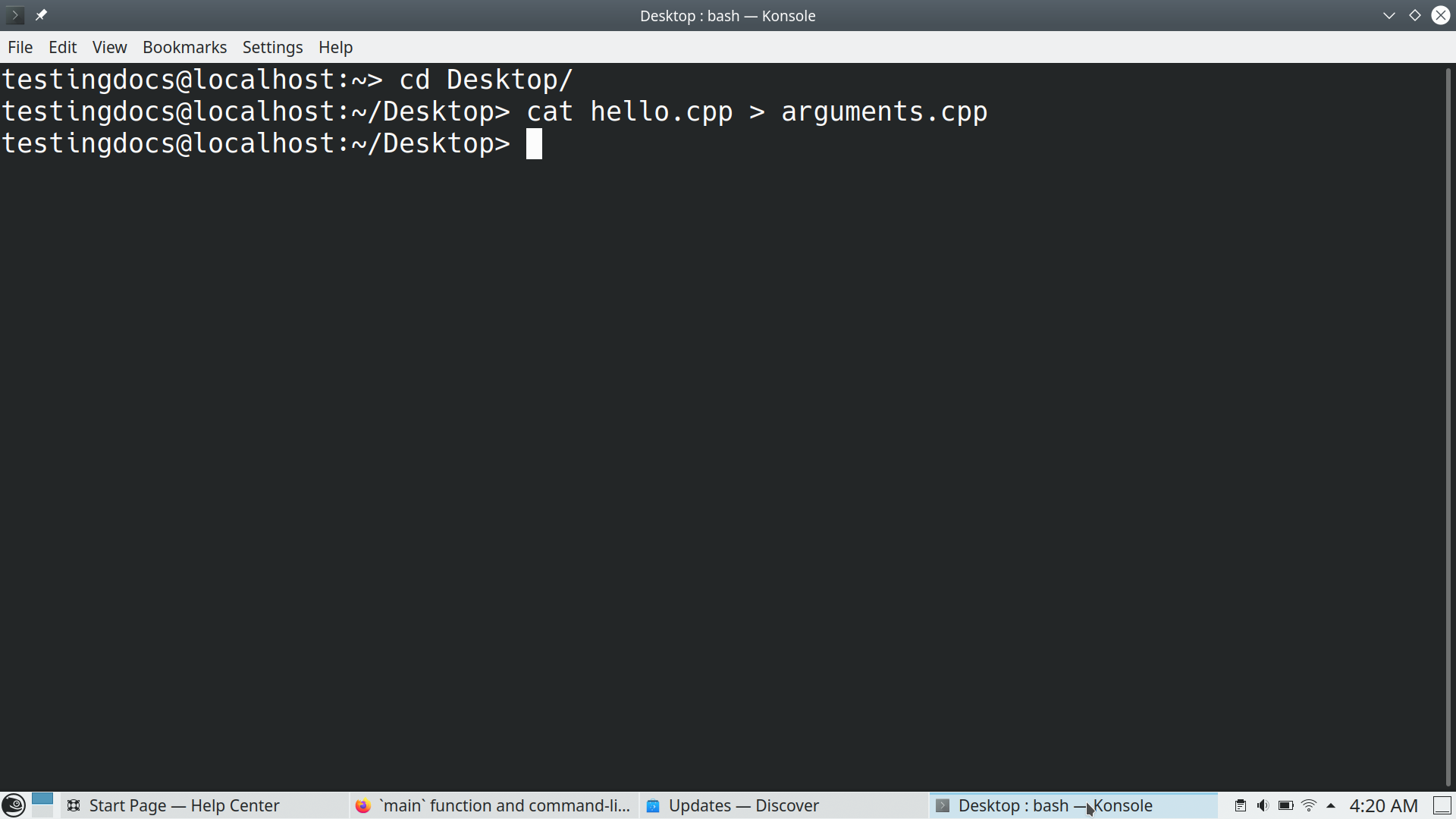
The cat command can also be used to create and copy file contents. For example, the below command creates a new file called arguments.cpp, and the file contents of the hello.cpp are copied to the new file.
The > operator redirects the file contents to the file instead of displaying on the standard output screen.
$ cat hello.cpp > arguments.cpp
–
Basic Linux Commands
Linux Basic Commands Tutorial page:
https://www.testingdocs.com/linux-basic-commands-tutorial/
More Information on Ubuntu Linux:
https://ubuntu.com/