mkdir Unix Command
mkdir Unix Command
In this tutorial, we will learn the mkdir Unix Command with examples. We can run the command on a Linux machine as well. To run the command, launch the Terminal or Konsole. mkdir is the short form for “make directory”. The mkdir command creates one or more directories.
Command Format
The command format:
$ mkdir <flags> directory_list
To know more about the command, type the man
$ man mkdir
The directory_list is the paths of the directories that the mkdir command creates. The user must have permission to write and execute permission on the parent directory of the “would be created directory”.
Examples
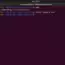
Simple command to create a folder called ‘automation’ under the present working directory.
$ mkdir automation
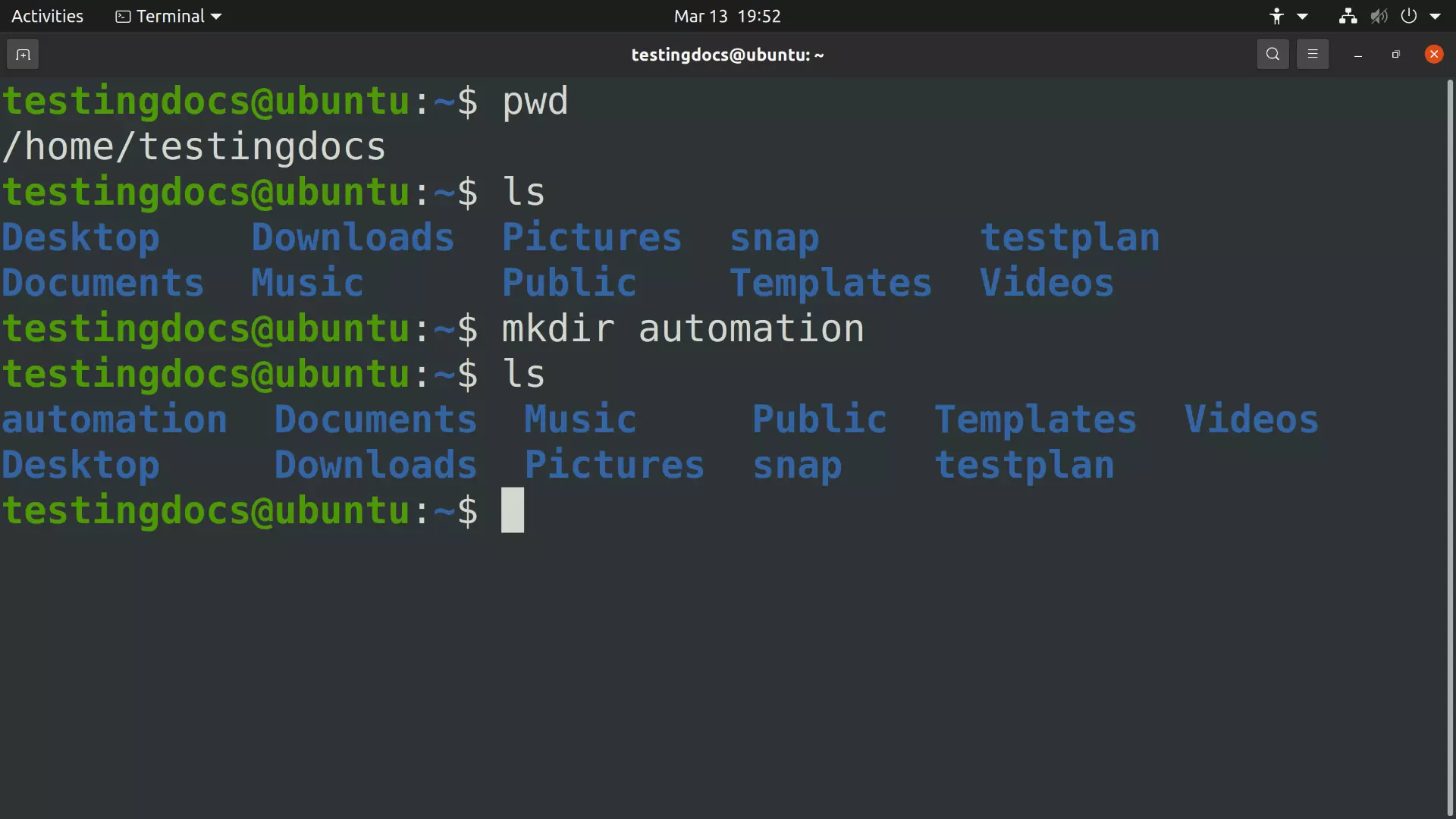
This command will create a directory called automation in the present working directory. We can use the pwd command to know the present working directory. To create under a specific directory, we need to change the directory using the cd command.
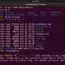
When we create a new directory using the mkdir command, two entries are automatically created. These directory entries are hidden by default.
The entries are:
- single dot( . )
- double dots( .. )
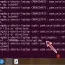
Create a sample directory with the mkdir command and list the contents with ls -a command.
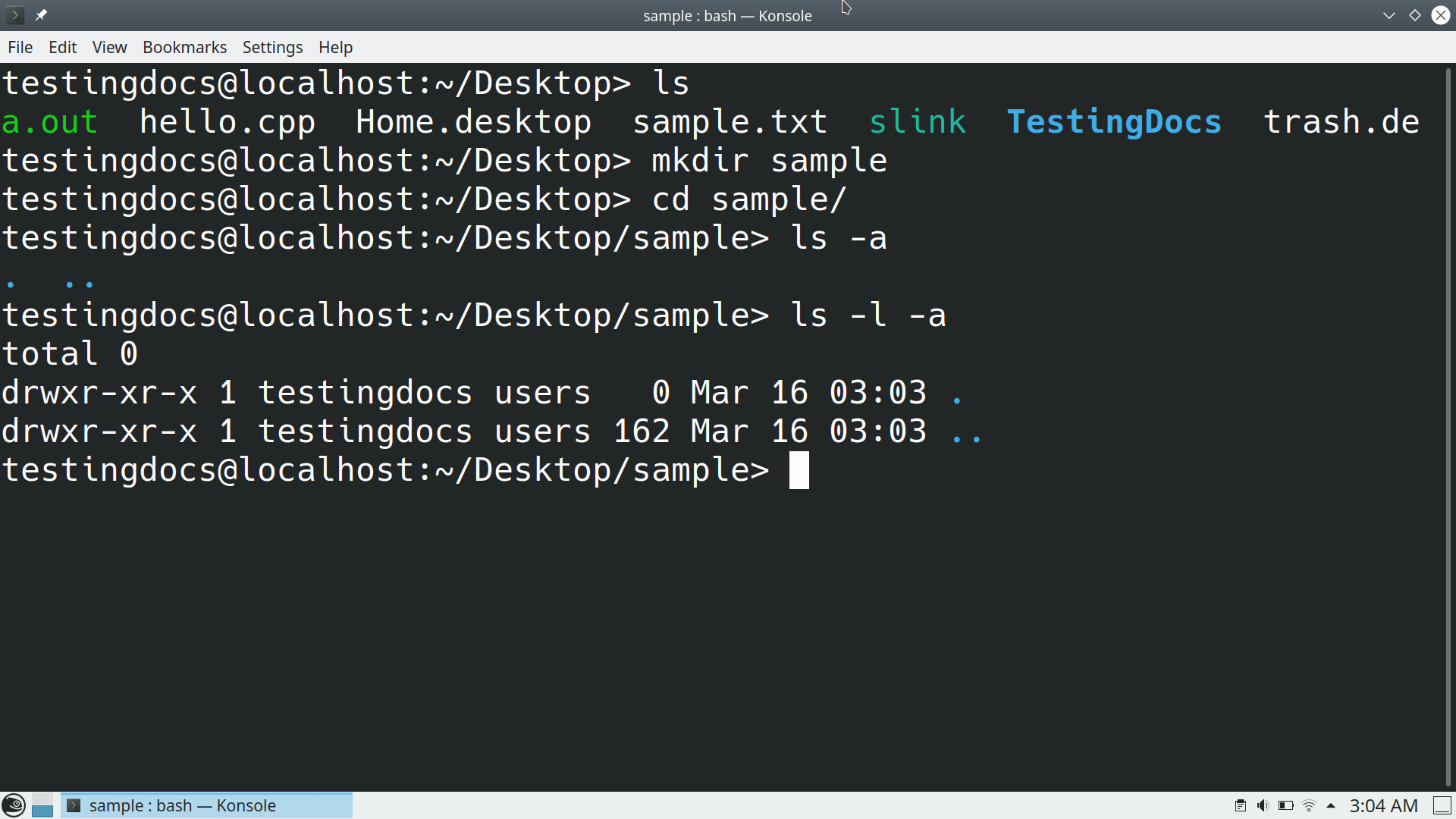
The single dot represents the current working directory itself.
The double dots represent the parent of the working directory.
-p parent
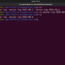
We can also create a parent directory with the mkdir command. We can use the -p option to create the parent directory of the subdirectory that we are creating.
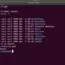
$ mkdir -p testplan/testcases
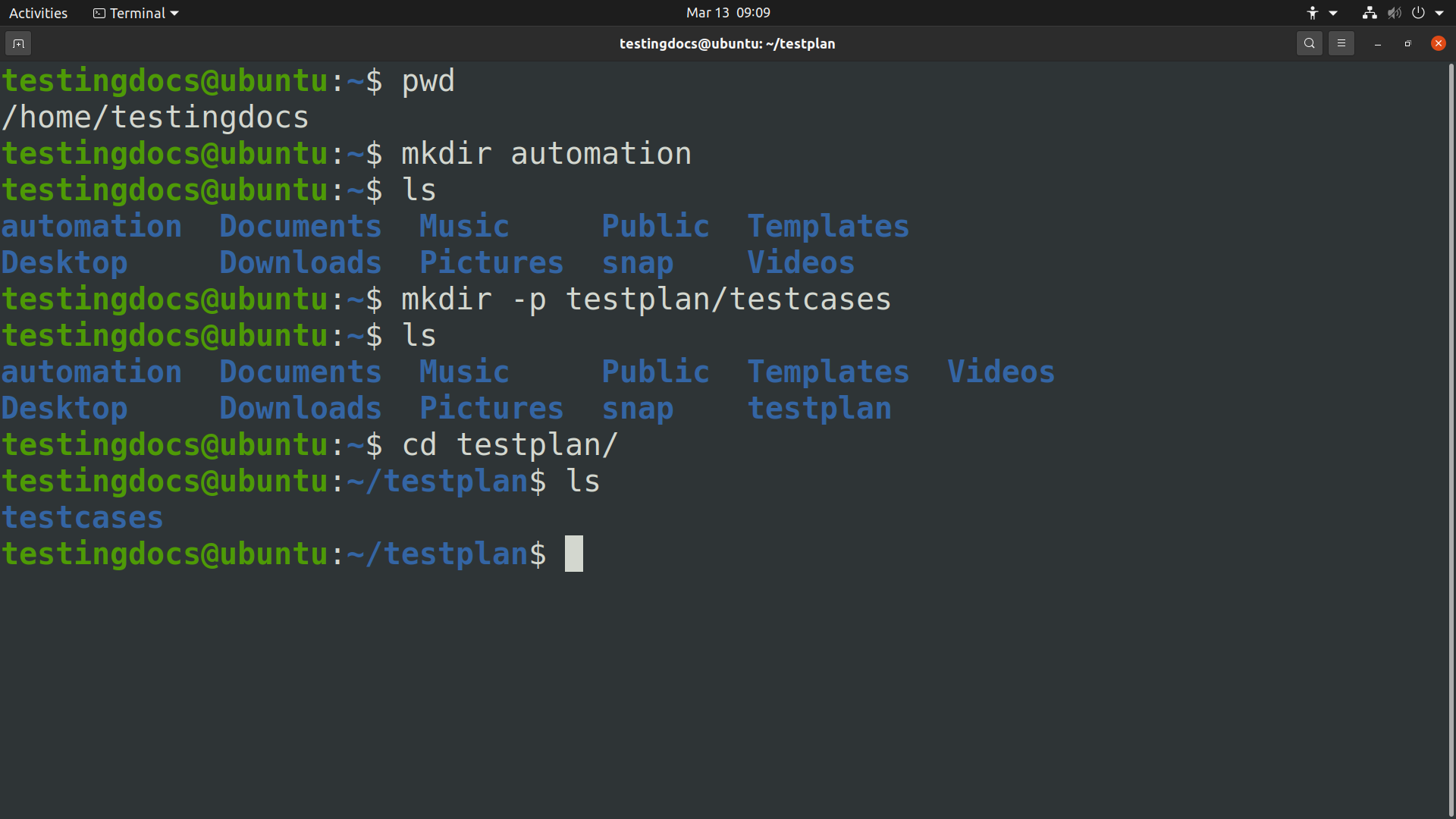
We can notice that both ‘testplan’ and ‘testcases’ directories are created by the command. In this example, ‘testcases’ is the subdirectory of the parent directory ‘testplan’.
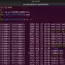
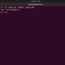
Now to create a directory under testplan we can omit the -p flag.
$ mkdir testplan/testresults
–
Linux Commands Tutorial page:
https://www.testingdocs.com/linux-basic-commands-tutorial/
More Information on Ubuntu Linux:
https://ubuntu.com/