Java Arithmetic Operators
Overview
Java arithmetic operators are symbols used in arithmetic calculations in programs. They are binary and require two operands to perform the calculations.
Arithmetic Operators
Java arithmetic operators are shown below:
| Arithmetic Operation |
Operator Symbol | Example |
| Addition
|
+ | a + b |
| Subtraction | – | a – b |
| Multiplication | * | a * b |
| Division | / | a / b |
| Modulus | % | a % b |
Order of Precedence
The order of precedence is from top to bottom in the table. For example, the expression inside the brackets/parenthesis is evaluated first.
| Arithmetic Operator |
Operation | Precedence |
| ( )
|
Brackets | Expressions in brackets are evaluated first. Nested the innermost are evaluated first. |
| * / % | Multiplication
Division Modulus |
The order of precedence. Left to Right. |
| + – | Addition
Subtraction |
Left to Right |
Example
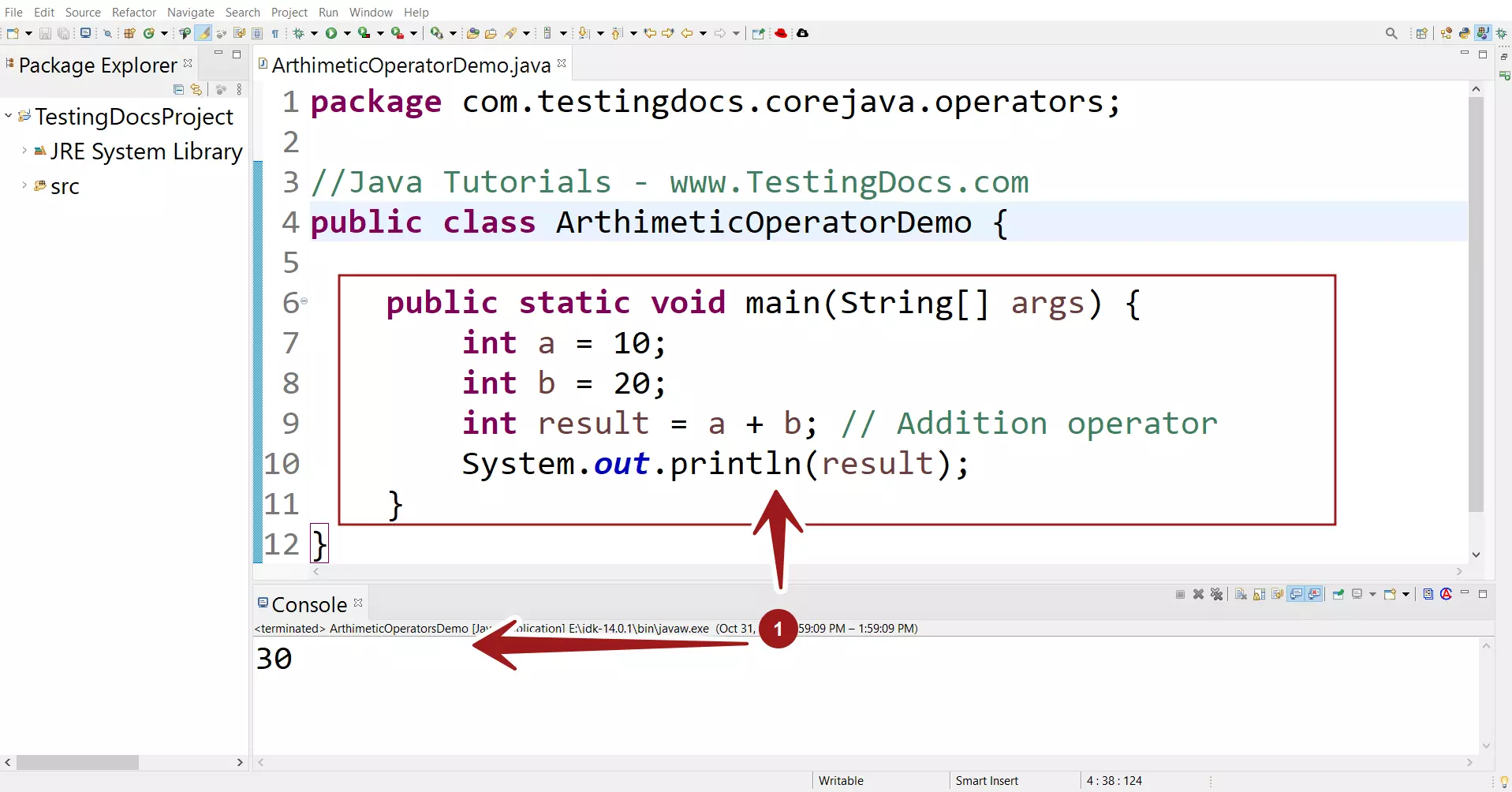
Let’s look at an example of Addition operator in a sample program. We will declare two variables of type int. We will sum the variables with the addition operator + . We print the result to the console.
public class ArthimeticOperatorDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 10;
int b = 20;
int result = a + b; // Addition operator
System.out.println(result);
}
}
Common Errors
Type mismatch error
Addition operator is a binary operator. It needs two operands to perform the calculation. Both the operands should be of the same type or compatible datatypes.
int a = 10;
double b= 2.0;
double result = a + b; // int and double are compatible types for + operator
System.out.println(result);
Initialized variables
Both the operands should be initialized properly.
int a = 10;
int b;
int result = a + b; // this would produce an error.
The addition statement would throw an error. The local variable b may not have been initialized.
—
Java Tutorials
Java Tutorial on this website:
https://www.testingdocs.com/java-tutorial/
For more information on Java, visit the official website :