Java Programming Language Features
Overview
In this tutorial, we will learn about Java Programming Language Features. Java is a general-purpose, object-oriented programming language.
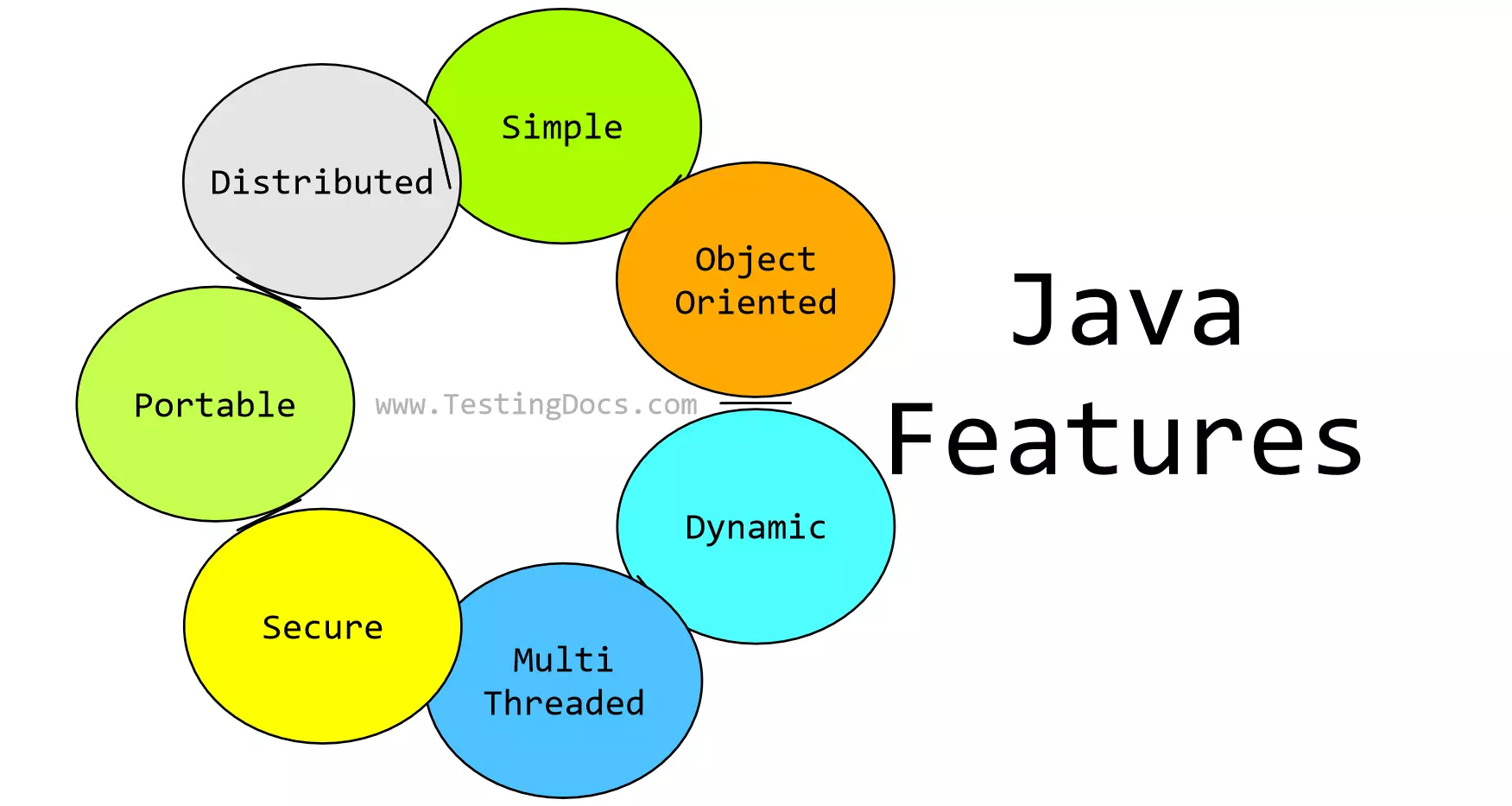
Java Features
Some of the Java programming language features are as follows:
- Simple
- Platform Independent
- Object-Oriented
- Compiled & Interpreted
- Robust
- Dynamic
- Multithreaded
- Secure
- Portable
- Distributed
Simple
Java is simple and easy to learn. A basic understanding of OOPS concepts is sufficient to learn and get started with the Java Language. Java is a simple language compared to C++. It has the same syntax but removes complex features like pointers, preprocessor header files, etc.
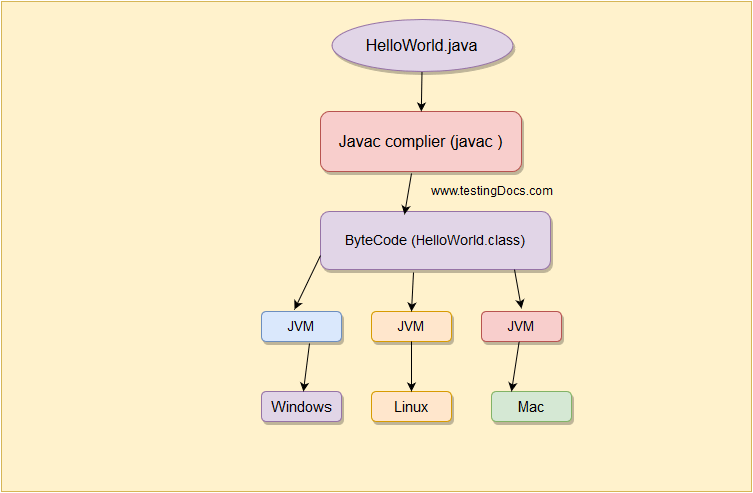
Platform Independent
Java code is compiled into platform-independent byte code. This byte code can run on Java Virtual Machine(JVM). The byte code is interpreted by a virtual Machine on whichever hardware platform it is being run. Thus Java is platform-independent and exhibits the Write Once, Run Anywhere(WORA) property.
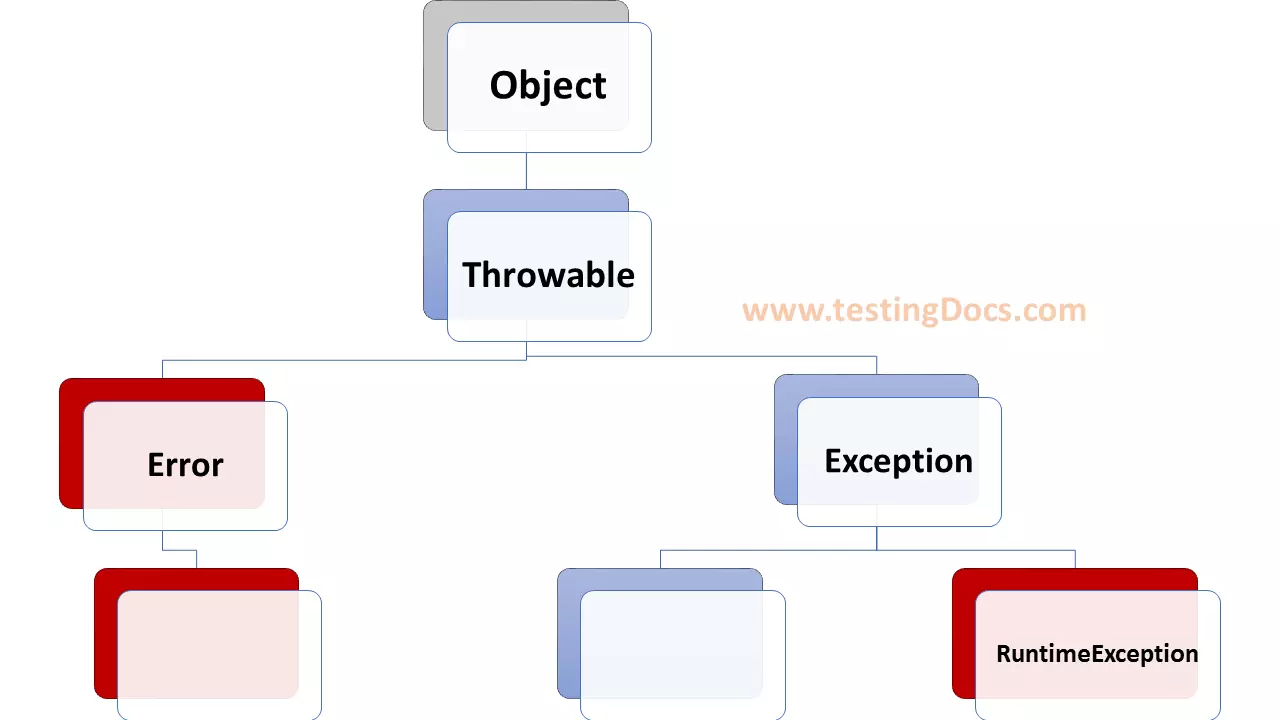
Object-Oriented
Almost everything in Java is an object. Objects are instances of class definitions. The Object class is the superclass for all classes in Java.
Multithreaded
Java supports the multi-threading feature. It is possible to write Java programs that can do multiple tasks simultaneously. We can create threads either by extending the Thread class or implementing the Runnable interface. This design feature allows developers to construct smoothly running interactive applications.
Dynamic
Java is capable of dynamically loading and linking new classes, objects, and methods.
Secure
Java supports strong Encryption algorithms and Authentication techniques. Java’s built-in security features enable programmers to develop virus-free applications.
Portable
Java programs can be easily moved from one machine to another irrespective of the host operating system and hardware. Java portability is because the Java compiler generates bytecode (JVM ) instructions that can run on any machine.
Distributed
Java can be used for creating distributed multi-tier applications on networks. Multi-tiered application functionality is separated into isolated tiers ( For example, the MVC pattern). Model-View-Controller pattern, the presentation logic in the view client layer, the business logic in the model data tier, and the controller to route the
client requests.
—
Java Tutorials
Java Tutorial on this website:
https://www.testingdocs.com/java-tutorial/
For more information on Java, visit the official website :