Java Strings
Overview
In this tutorial, we will learn about Java Strings. Java String represents a sequence of characters.
Create a String
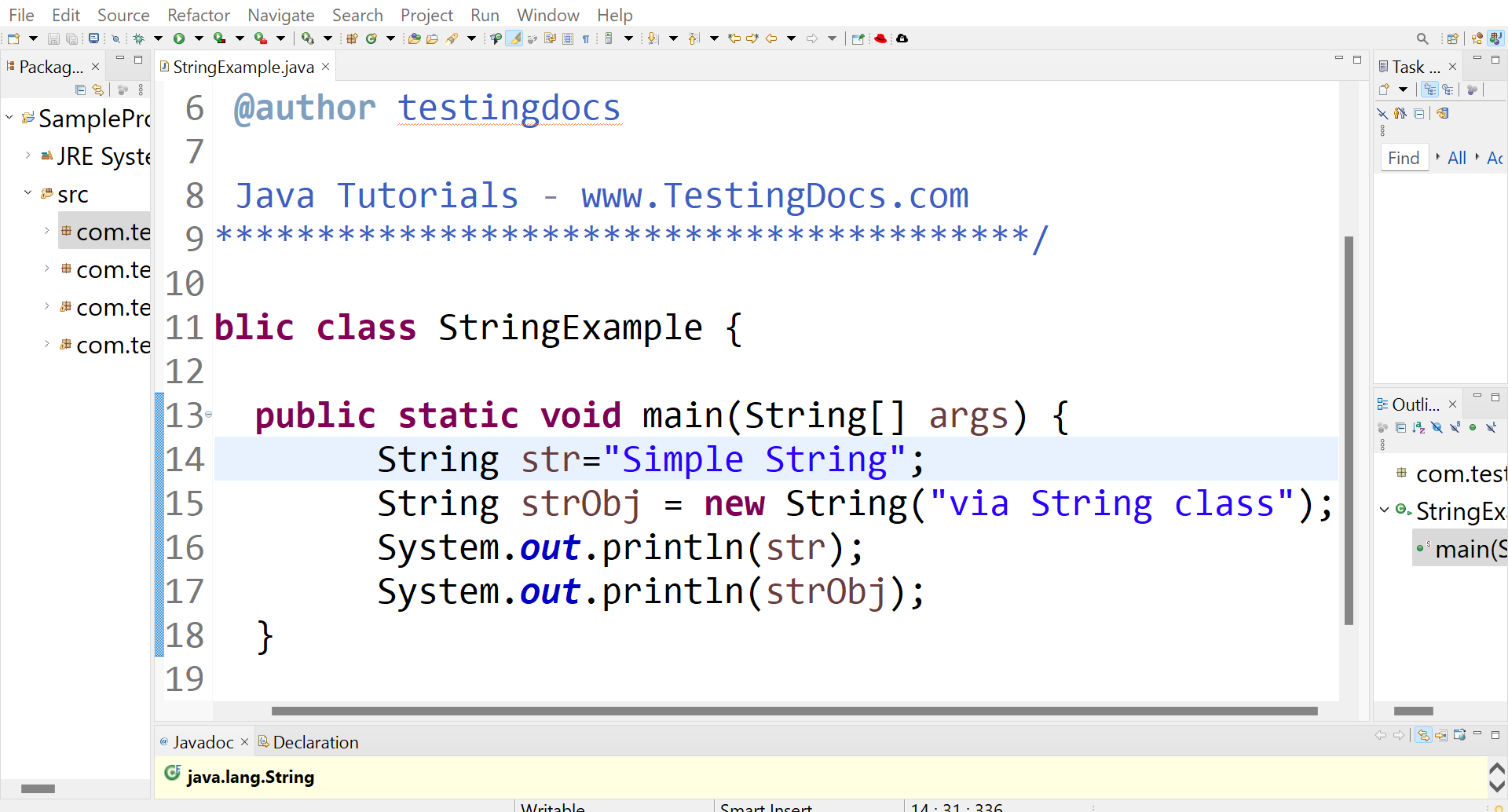
The simplest way to create a String is to enclose the string literal in quotes and assign the value to a String object.
String str = “Simple String”;
Alternatively, Strings can be created through String class constructors. Creation of a String in this method
require the use of the new operator.
String str = new String(“via String class”);
In Java programming language, Strings are immutable. It means that we cannot change the value of the string.
The main reasons behind this are better performance and security. Creating a copy of an existing String is easier as there is no need to create a new instance but can be easily created by pointing to an already existing String. Using String as a key for Hashtable guarantees that there will be no need for rehashing because of object change. Using String in a multi-threaded environment is safe by itself and we need not take any precautionary measures.
Strings are stored in a special memory called a String Pool. A String Pool is a separate memory area where all the strings which are defined are stored.
Example
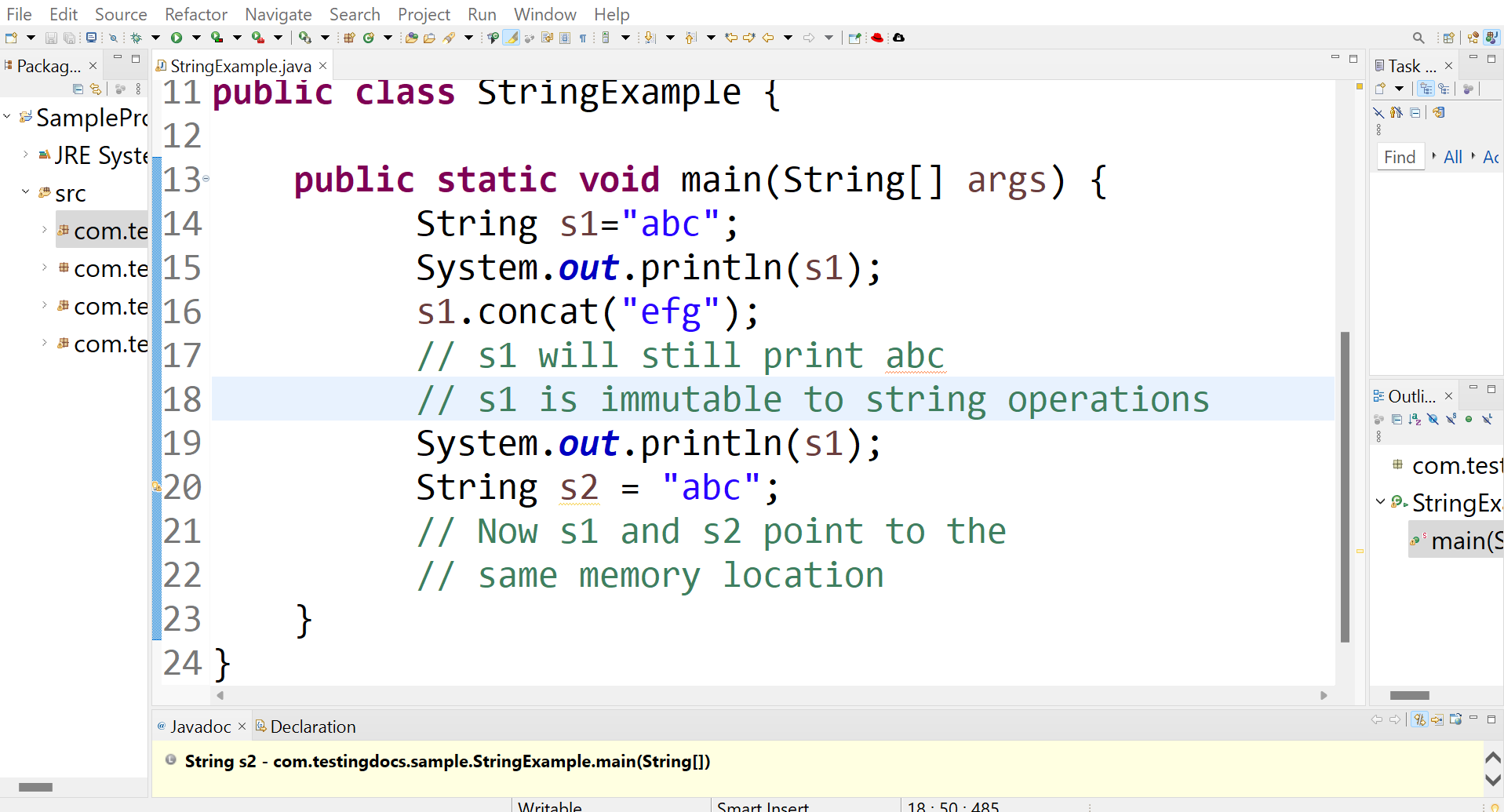
String s1 = “abc”;
System.out.println(s1);
s1.concat(“efg”);
// s1 will still print abc
// s1 is immutable to string operations
System.out.println(s1);
This string(s1) will be stored in memory at a particular address. When we define a new String with the same array of characters like
String s2 = “abc”;
// s1 and s2 point to the
// same memory location
The JVM will check the string in the String Pool. If two Strings match the JVM will refer s1 memory address to s2. The s1 and s2 refer to the same string in the same memory location.
If Strings are mutable changing s1 would reflect s2 as well. To avoid this Strings are immutable.
—
Java Tutorials
Java Tutorial on this website:
https://www.testingdocs.com/java-tutorial/
For more information on Java, visit the official website :