Linux Command Syntax
Overview
This tutorial will teach us about Linux Command Syntax and sample Linux commands.
Linux Shell
In Linux, a shell is a command-line interpreter. It provides an interface between users and the Linux kernel and executes Linux commands and programs. For example, if a user enters the ls command, the shell executes the ls command.
The shell has many utilities built into the shell called builtins.
The shell parses the command and finds the program or utility to execute. It passes the command line switches, arguments to the program as part of a new process.
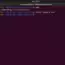
To check what shell has been configured on the machine:
$ echo $SHELL
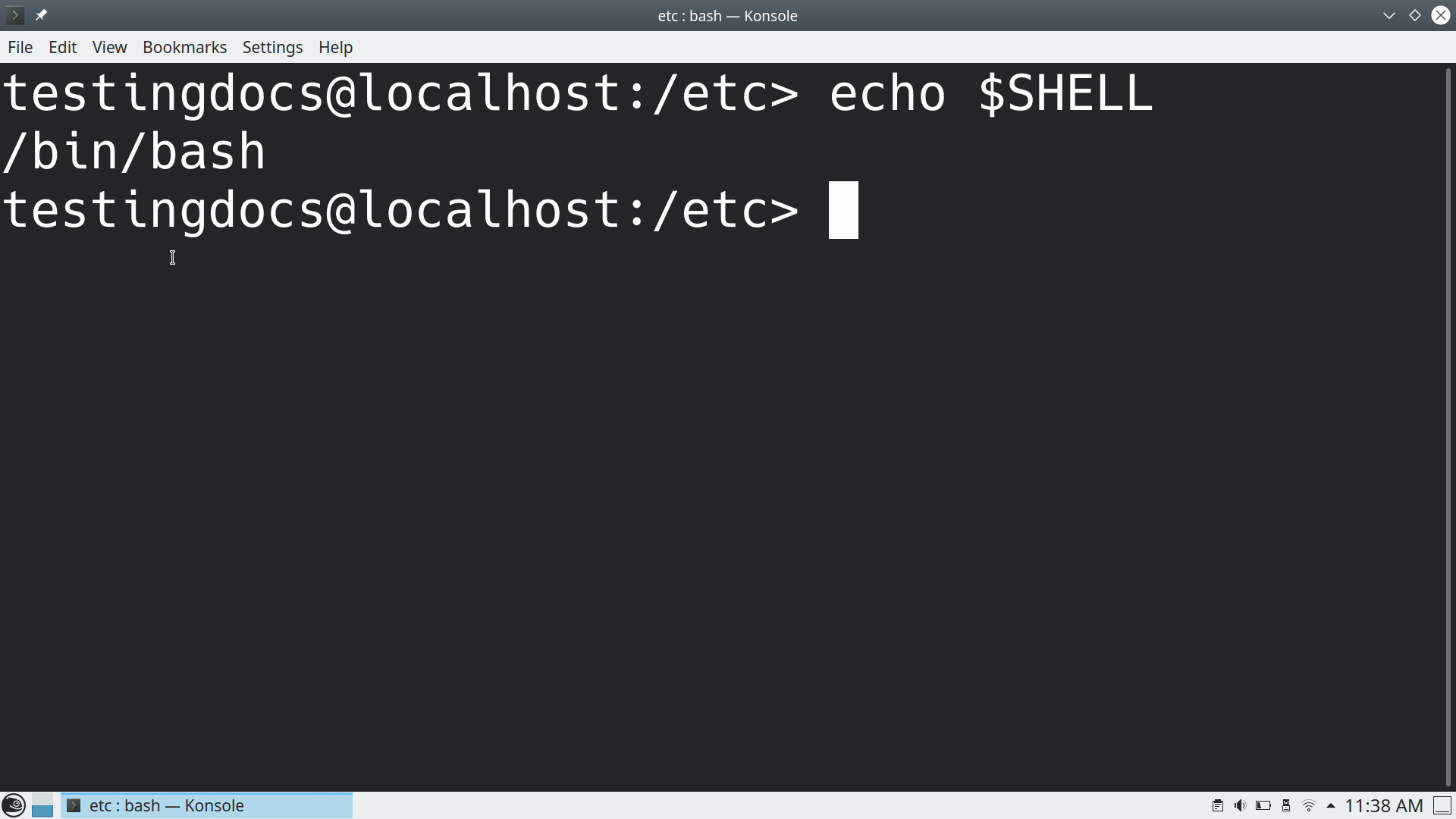
Different Linux distributions provide a GUI wrapper for the shell. For example, Terminal is the default shell application on Ubuntu Linux distribution. Konsole is the default GUI application for OpenSuse.
Linux Command Syntax
$ command command-flags [command-arg1] [command-arg2]
Command
Linux command is the utility or program that is executed by the shell.
Command flags or Switches
Command flags, options or switches alter or modify the effects of the Linux command. Linux commands require prefix switches with a hyphen symbol.( – )
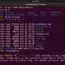
$ pwd -P
Here pwd is the Linux command. -P is the command line switch for the command. We can also group multiple command switches together with a single hyphen.
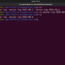
$ ps -aux
Command Arguments
Command arguments are data, objects, text, digits, etc that the Linux command acts on. Command arguments are optional. Linux commands can be executed with or without command arguments. Some Linux commands require mandatory arguments that we need to pass for the command to work.
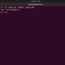
For example, the cp Linux command requires two command arguments. The existing file to copy and the target name of the copy of the file.
$ cp exisitingFile.txt newFileCopy.txt
—
Linux Commands Tutorial page:
https://www.testingdocs.com/linux-basic-commands-tutorial/
More Information on Ubuntu Linux:
https://ubuntu.com/