Introduction to SQL(Structured Query Language)
Introduction
SQL(Structured Query Language), pronounced as “sequel” or S.Q.L, is a query language used to access, interact with, and manipulate relational databases. A good understanding of SQL will help us access and manipulate data in databases like Oracle, MySQL, MS SQL Server, MS Access, IBM DB2, etc.
SQL has rules of grammar and syntax like normal English and can be easily understood. SQL is an ANSI standard. (American National Standards Institute) .
Features of SQL
SQL is a standard language to access and manipulate relational databases. Some of the features are as follows:
- SQL usage is extremely flexible and uses a free-form syntax. ( The same SQL query can be written in a variety of ways)
- SQL allows operations to create, update, and delete database objects. Database objects like tables, views, etc.
- SQL allows operations to insert, update, and delete data. SQL is a query language to retrieve and aggregate data.
- The SQL statements can be embedded in other high-level programming languages. like C, Java, etc.
SQL Statements
Most of the actions we need to perform on a database are done with SQL statements. Some database systems require a semicolon(;) at the end of each SQL statement. The semicolon (;) is the standard way to separate each SQL statement.
The SELECT statement is used to select data from a database. For example, the following SQL SELECT statement will select all the records in the emp database table:
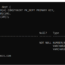
SELECT * FROM emp;
SQL is not case-sensitive. For example, both the SQL queries are the same.
SELECT * FROM emp;
select * from emp;
Example SQL Query
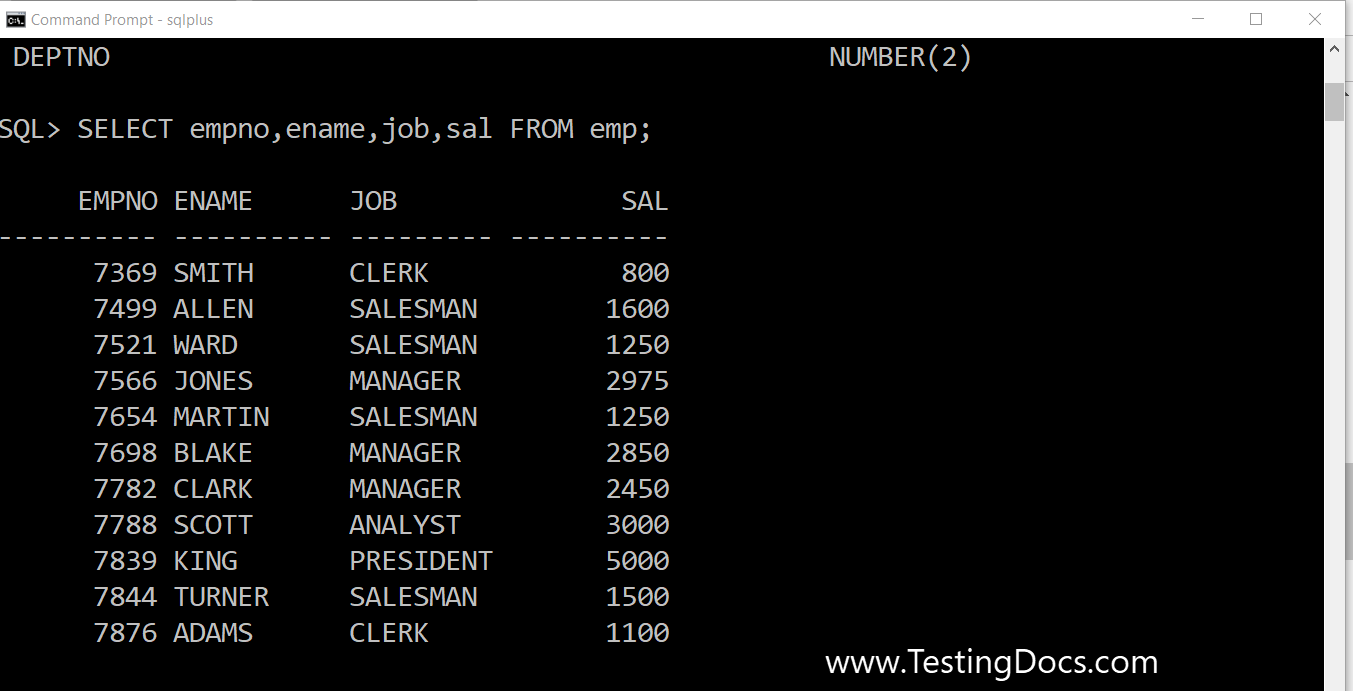
We can specify the exact columns that we want in the SQL statement. Let’s write a simple query to retrieve employees’ empno, name, salary, and job details from the emp table.
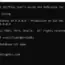
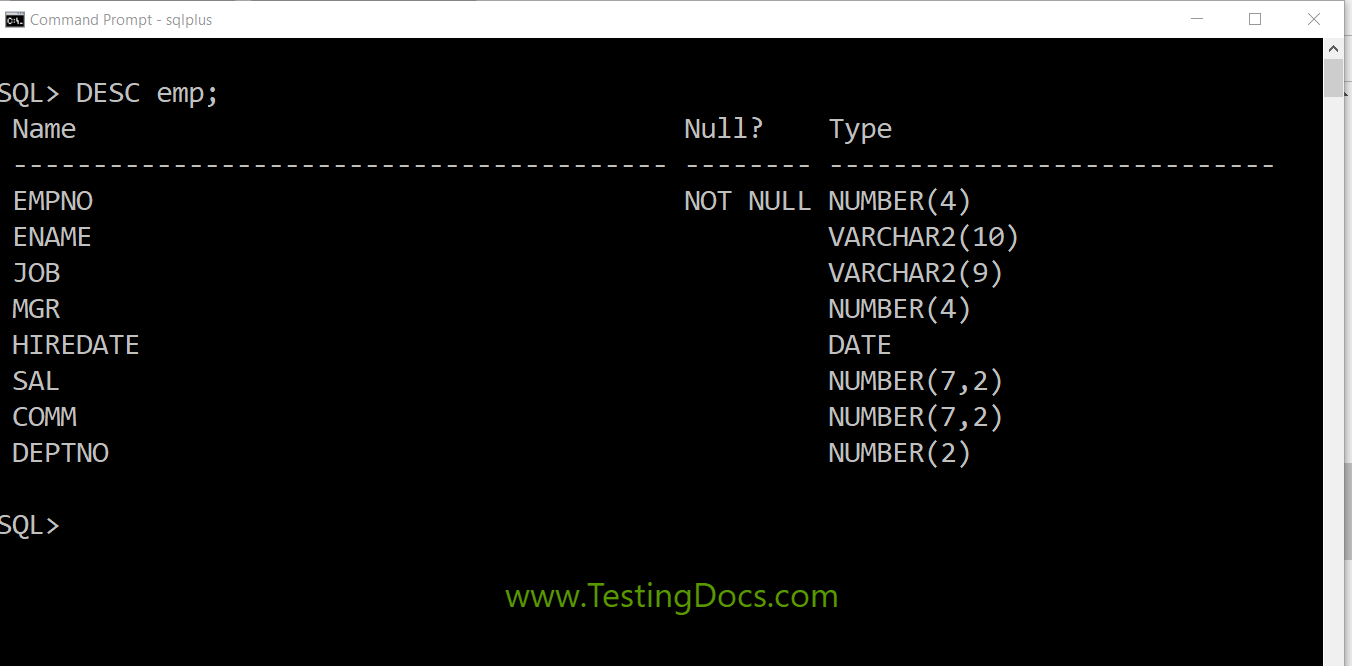
The table structure of the emp table is shown below:
SQL> DESC emp; Name Null? Type ----------------------------------------- -------- ---------------------------- EMPNO NOT NULL NUMBER(4) ENAME VARCHAR2(10) JOB VARCHAR2(9) MGR NUMBER(4) HIREDATE DATE SAL NUMBER(7,2) COMM NUMBER(7,2) DEPTNO NUMBER(2)
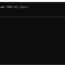
SQL> SELECT empno,ename,job,sal FROM emp;
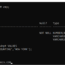
Query result:
SQL> SELECT empno,ename,job,sal FROM emp; EMPNO ENAME JOB SAL ---------- ---------- --------- ---------- 7369 SMITH CLERK 800 7499 ALLEN SALESMAN 1600 7521 WARD SALESMAN 1250 7566 JONES MANAGER 2975 7654 MARTIN SALESMAN 1250 7698 BLAKE MANAGER 2850 7782 CLARK MANAGER 2450 7788 SCOTT ANALYST 3000 7839 KING PRESIDENT 5000 7844 TURNER SALESMAN 1500 7876 ADAMS CLERK 1100
SQL Commands
SQL commands can be divided into different types.
https://www.testingdocs.com/types-of-sql-commands/
—
Database Tutorials on this website:
https://www.testingdocs.com/oracle-database-tutorials-for-beginners/
More information about Oracle Database:
https://www.oracle.com/database/