Exception handling in Java
Overview
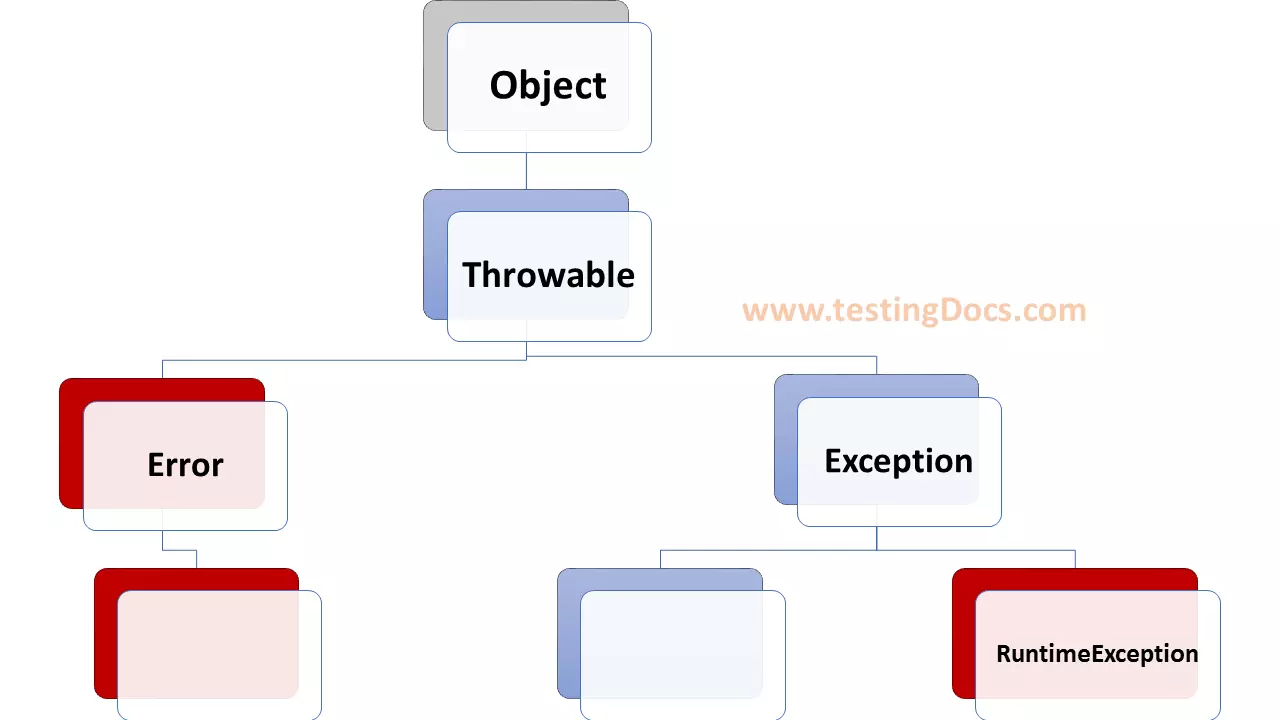
In this post, we will discuss single exception handling in Java. Errors occur in java programs as in most things in real life. Also, when an error occurs in a running Java program we say that an exception has occurred. Furthermore, when this happens an Exception object is created and “thrown”. This can be caught or not, depending on the kind of Exception it is and on the program.
try/catch block
It is easy to generate an exception as shown in the below code snippet.The below code will generate a NullPointerException which will be thrown. Also, we can catch this exception and therefore prevent the program from abnormal terminating. To catch an exception if it arises you include the statements that might throw the exception in a try block. Furthermore, the program will continue with the rest of the code after handling the exception.
public class ExceptionExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// ExceptionExample
try
{
throw new NullPointerException() ;
}
catch(NullPointerException npe)
{
npe.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
When a try block is specified, we need to either specify the catch handler or the finally block.
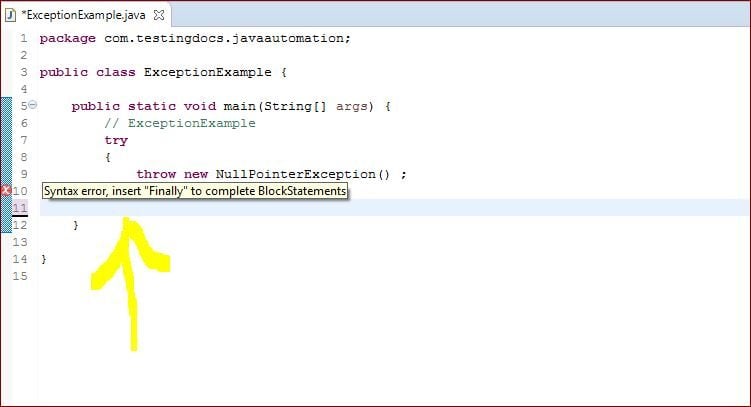
When we catch an exception we name the class of the exception and give a variable that will have that type. Within the body of the catch clause we can send the Exception object messages. Also, when an exception is thrown in a try block, the execution of the try is abandoned immediately and the system searches for a handler in the catch block of the type of exception that was thrown.
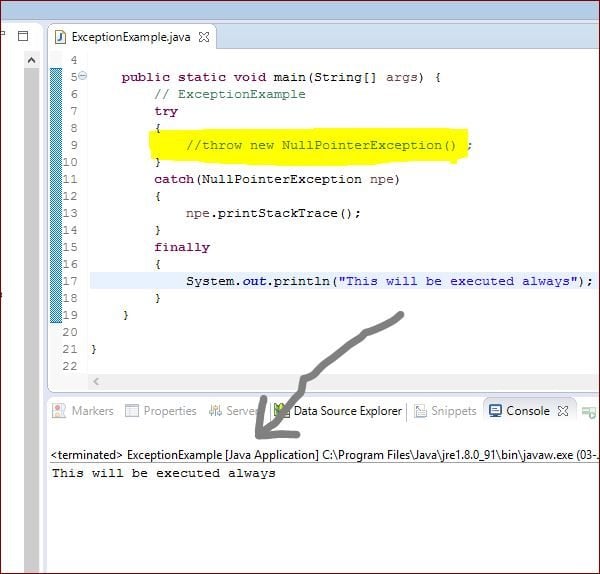
finally block
Java finally block is a block that is used to execute important clean-up code such as closing a connection, browser driver instance, etc. Also, finally block is always executed regardless of exception is thrown or not as shown in the below picture.
—
Java Tutorials
Java Tutorial on this website:
https://www.testingdocs.com/java-tutorial/
For more information on Java, visit the official website :