Java Arrays
Overview
In this tutorial, we will learn Java Arrays. In Java, an array is a data structure that stores values of the same data type. Each element in the array can be accessed using the index.
We can use the array data structure if we know the array size up front.
Declare an array
We can declare an array using the following syntax:
datatype[] arrayVariable;
For example, to declare an integer array:
int[] arr; // declare an integer array
Notice that the size of the array is not part of this declaration.
Create an array
We can create an array with the new operator.
arr = new int[3];
We have created an array with 3 elements.
Initialize array elements
We can initialize the array elements with the index. In Java, the array index starts with 0.
arr[0]=10;
arr[1]=20;
arr[2]=30;
Alternatively, we can use the below syntax to create an initialize the array elements.
int[] arr = {1,2,3,4,5};
Example
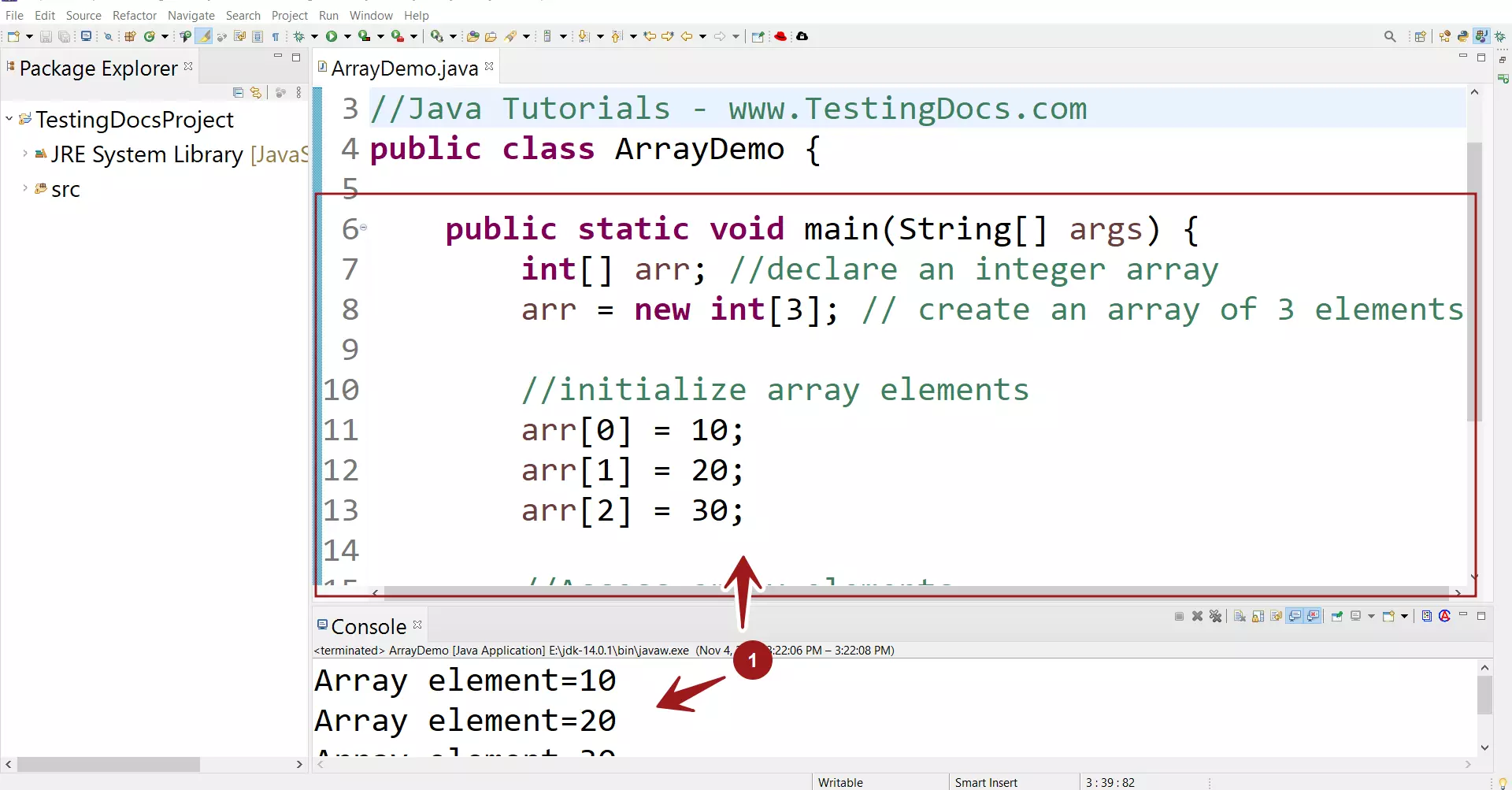
//Java Tutorials - www.TestingDocs.com
public class ArrayDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr; //declare an integer array
arr = new int[3]; // create an array of 3 elements
//initialize array elements
arr[0] = 10;
arr[1] = 20;
arr[2] = 30;
//Access array elements
System.out.println("Array element =" + arr[0]);
System.out.println("Array element =" + arr[1]);
System.out.println("Array element =" + arr[2]);
}
}
Example
Now, Let’s see how to declare an array with the String data type.
String[] strArray = new String[6];
OR
String[] strArray = {“Java”,”Eclipse”,”IntelliJ”,”J2EE”,”JMS”,”MySQL”};
—
Java Tutorials
Java Tutorial on this website:
https://www.testingdocs.com/java-tutorial/
For more information on Java, visit the official website :