Java Relational Operators
Overview
Java relational operators are symbols that compare operands. They are binary and require two operands to perform the calculations.
Relational Operators
Java relational operators are shown below:
| Relational Operation |
Operator Symbol | Example |
| Equal To
|
== | a == b |
| Not equal to | != | a != b |
| Greater Than | > | a > b |
| Greater Than or Equal To | >= | a >= b |
| Less Than | < | a < b |
| Less Than or Equal To | <= | a <= b |
Example
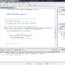
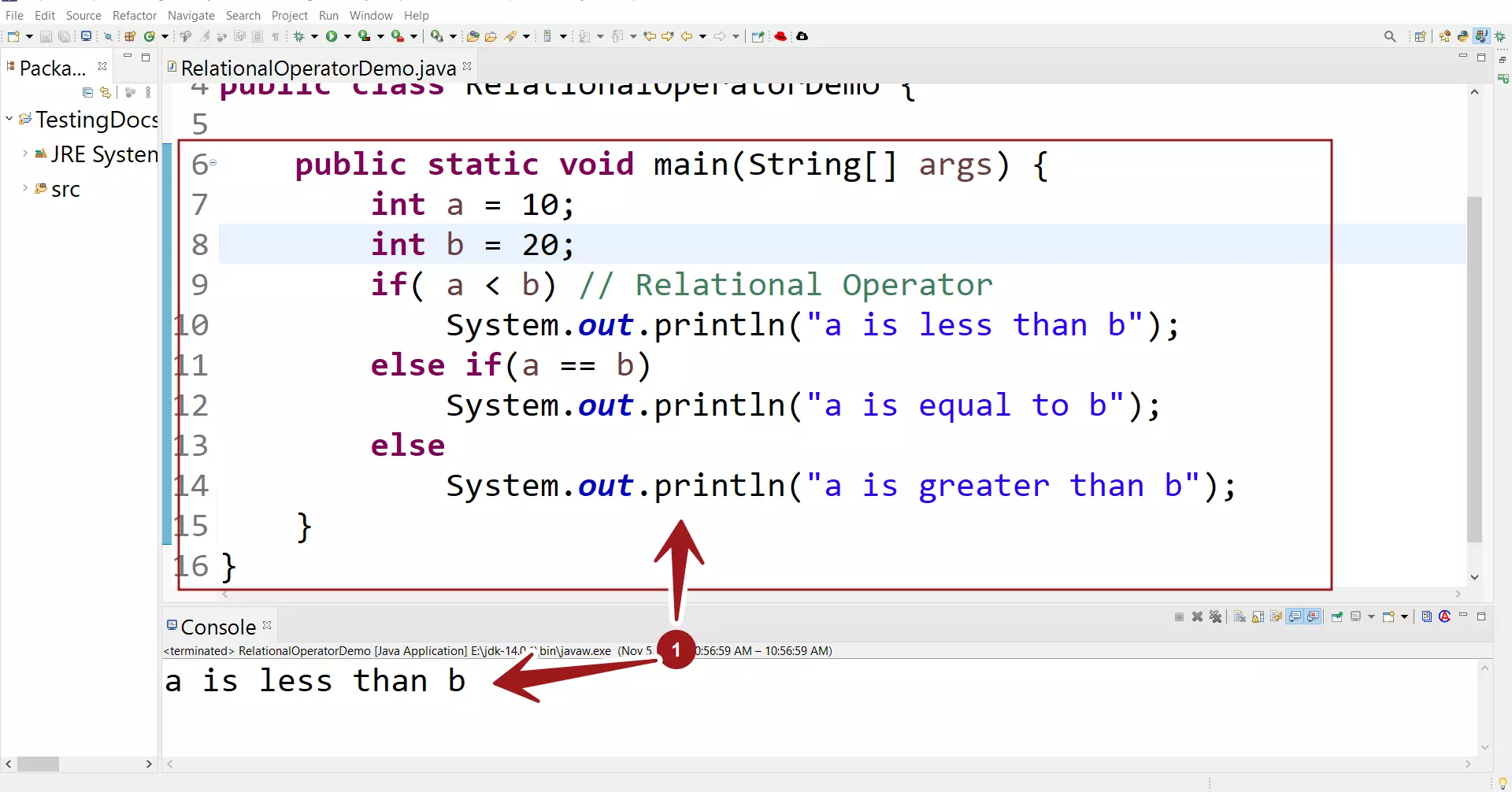
Let’s look at an example of Relation operator in a sample program. We will declare two variables of type int. We will compare if a is less than b in a if statement. If a < b then the expression evaluates to true.
public class RelationalOperatorDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 10;
int b = 20;
if( a < b) // Relational Operator
System.out.println("a is less than b");
else if(a == b)
System.out.println("a is equal to b");
else
System.out.println("a is greater than b");
}
}
Based on the values, a variable holds the value of 10 and b variable holds the value of 20. Since, 10 < 20 the expression a < b evaluates to true. The if statement would be executed and the else statements will not execute.
—
Java Tutorials
Java Tutorial on this website:
https://www.testingdocs.com/java-tutorial/
For more information on Java, visit the official website :