Read from Standard Input using Scanner
Introduction
In this article, we will learn to read from standard input in Java. First of all, one way to read input from standard input in Java is by using the Scanner class and specifying the Input Stream as System.in. A simple text scanner which can parse primitive types and strings using regular expressions.
Scanner
A Scanner breaks its input into tokens using a delimiter pattern, which by default matches white space. The resulting tokens may then be converted into values of different types using the various next methods.
For example, this code allows a user to read a number from System.in:
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in); int i = scanner.nextInt();
Another sample example is shown in below :
Consider Input: months 12
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
String sampleString = scanner.next();
int sampleInt = scanner.nextInt();
scanner.close();
System.out.println("String is: " + sampleString);
System.out.println("Int is: " + sampleInt);
Java Platform API for Scanner for further reference :
https://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/java/util/Scanner.html
Code Example
package com.testingdocs.javaautomation;
import java.util.*;
public class ScannerExample {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
try
{
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
int N = in.nextInt();
for(int i=1; i<= 20; i++)
System.out.println( N + " x " + i + " = " + N*i);
}
catch(InputMismatchException ime)
{
System.out.println("Input mismatch Exception");
}
catch(Exception e)
{
System.out.println("Exception occurred");
}
}
}
Output for the above program for
Test case : Input value 9 is :
9 x 1 = 9
9 x 2 = 18
9 x 3 = 27
9 x 4 = 36
9 x 5 = 45
9 x 6 = 54
9 x 7 = 63
9 x 8 = 72
9 x 9 = 81
9 x 10 = 90
9 x 11 = 99
9 x 12 = 108
9 x 13 = 117
9 x 14 = 126
9 x 15 = 135
9 x 16 = 144
9 x 17 = 153
9 x 18 = 162
9 x 19 = 171
9 x 20 = 180
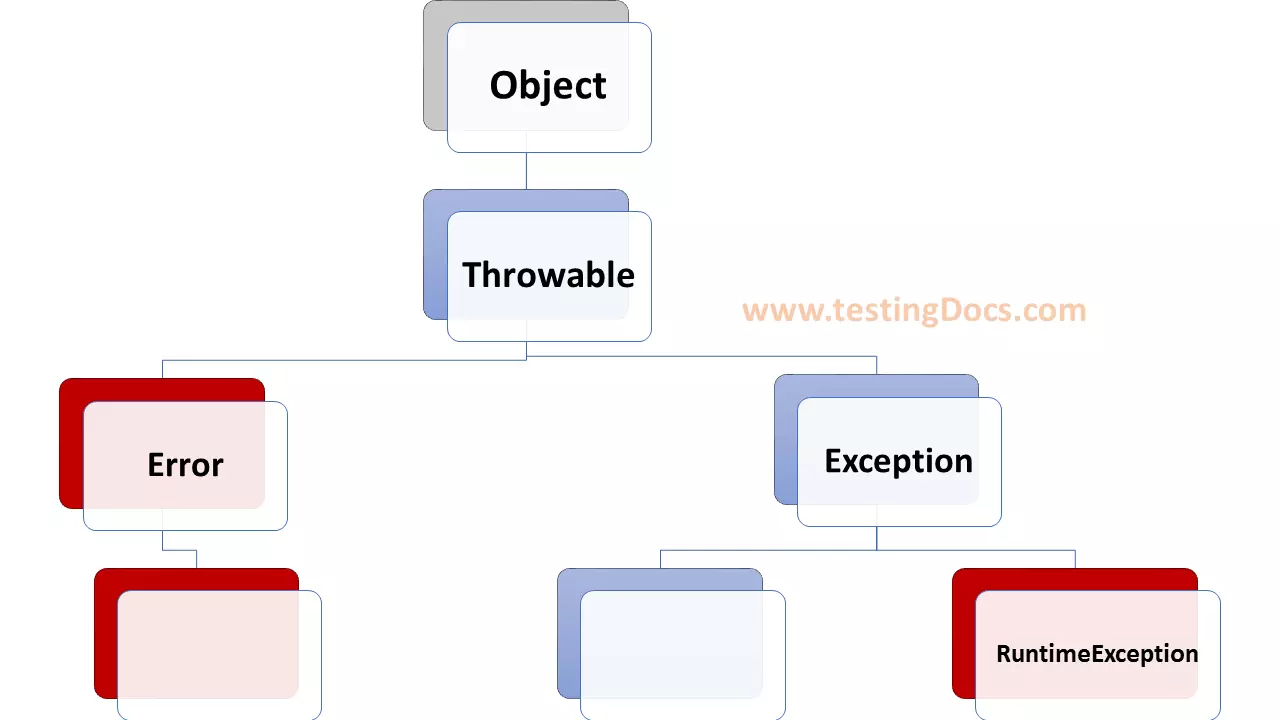
Invalid inputs the program throws an exception. In java exception is a class:
The class Exception and its subclasses are a form of Throwable that indicates conditions that an application might want to catch. The class Exception and any subclasses that are not also subclasses of RuntimeException are checked exceptions.
Checked exceptions need to be declared in a method or constructor’s throws clause if they can be thrown by the execution of the method or constructor and propagate outside the method or constructor boundary.
Java API page for more details:
https://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/java/lang/Exception.html
—
Java Tutorials
Java Tutorial on this website:
https://www.testingdocs.com/java-tutorial/
For more information on Java, visit the official website :