Java switch statement
Overview
Java switch statements are control structures used when we need to make multiple decisions in the Java program. We can replace the if-else-if ladder with switch statements.
Syntax
switch(){
case match1:
//code statements
break; // this is optional
case match2:
//code statements
break; // this is optiona;
…
default :
// code statements when no match
}
The break statement in the case block is optional. The purpose of the break statement is to execute only one case block. Upon break statement, the control jumps to the statement after the switch statement. When we omit the break statement in the case block, the next case statement is executed.
Java switch statement
switch statement can have a number of possible execution paths. Use switch to specify many alternative blocks of code to be executed.
Example:
public class SwitchCaseDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int weekday = 3;
switch (weekday) {
case 1:
System.out.println("Sunday");
break;
case 2:
System.out.println("Monday");
break;
case 3:
System.out.println("Tuesday");
break;
case 4:
System.out.println("Wednesday");
break;
case 5:
System.out.println("Thursday");
break;
case 6:
System.out.println("Friday");
break;
case 7:
System.out.println("Saturday");
break;
default:
System.out.println("Not in week!! ");
break;
}
}
}
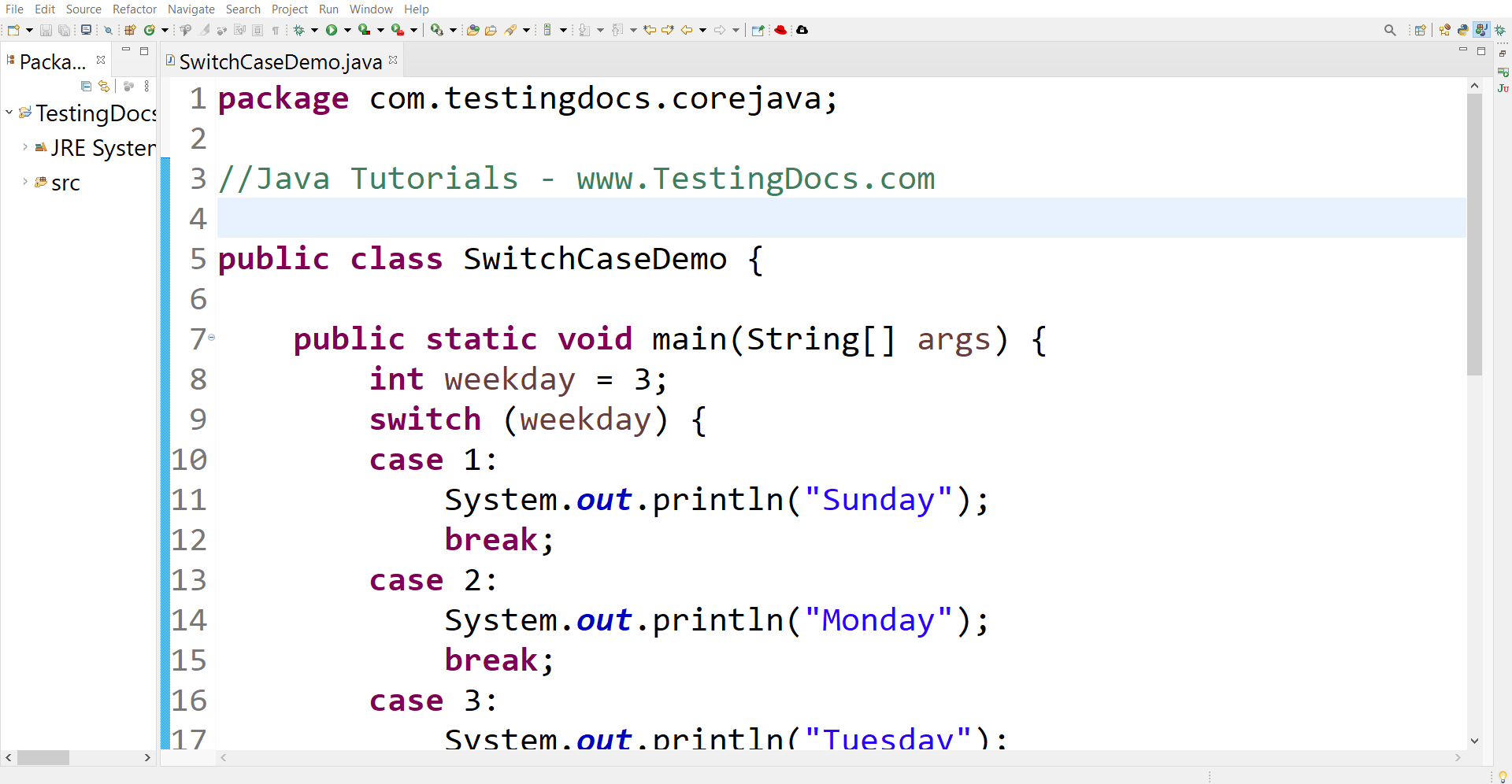
The output of the program is:
Tuesday
No break statements
Now, let’s omit the break statements in the case blocks an see what happens to the output.
//Java Tutorials - www.TestingDocs.com
public class SwitchCaseDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int weekday = 3;
switch (weekday) {
case 1:
System.out.println("Sunday");
break;
case 2:
System.out.println("Monday");
break;
case 3:
System.out.println("Tuesday");
case 4:
System.out.println("Wednesday");
case 5:
System.out.println("Thursday");
case 6:
System.out.println("Friday");
case 7:
System.out.println("Saturday");
default:
System.out.println("Not in week!! ");
break;
}
}
}
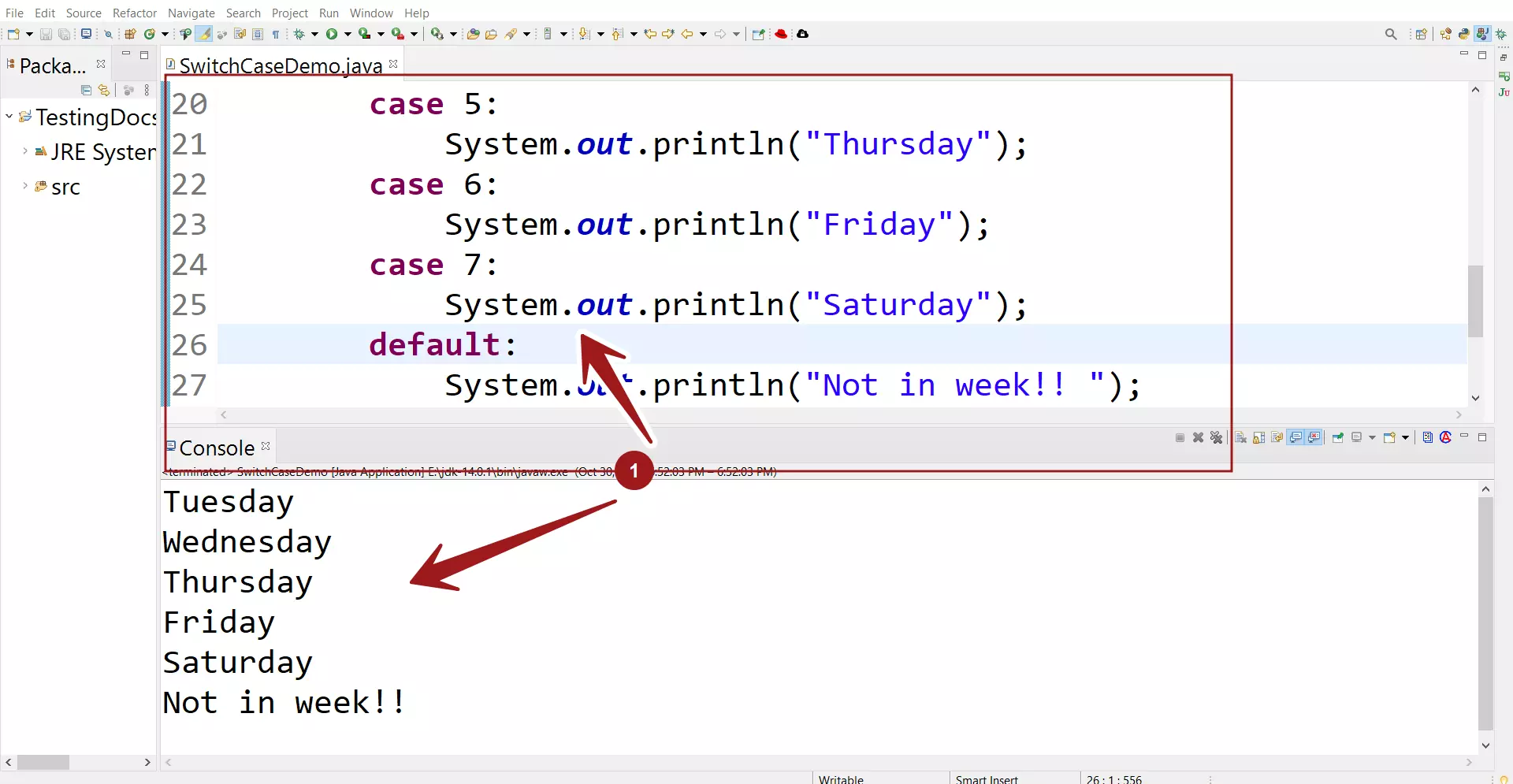
Tuesday
Wednesday
Thursday
Friday
Saturday
Not in week!!
We can clearly notice that all the case statements got executed, which is not the intended output.
In some cases, we may also have empty case blocks. In this case we are matching the alphabet character for both uppercase and lowercase.
case ‘a’:
case ‘A’:
—
Java Tutorials
Java Tutorial on this website:
https://www.testingdocs.com/java-tutorial/
For more information on Java, visit the official website :