JUnit Annotations order
Introduction
JUnit annotations are used to setUp and tearDown test fixtures. Different annotations in
JUnit4 are:
- @BeforeClass
- @AfterClass
- @Before
- @After
@BeforeClass and @AfterClass
@BeforeClass annotated method will be executed once before all the tests in the class. This method would be used to perform one time initialization.
On the other hand, @AfterClass annotated method will be executed once after all the tests in the class. This method is used to release any resources acquired during the tests etc.
@Before and @After
@Before annotated method will run before each test method in the class. For example, if you have 3 test annotated method, @Before method will run 3 times before each @Test annotated method.
On the other hand, @After annotated method will run after each test method in the class.
@Test annotation can be found here: JUnit @Test annotation
Example
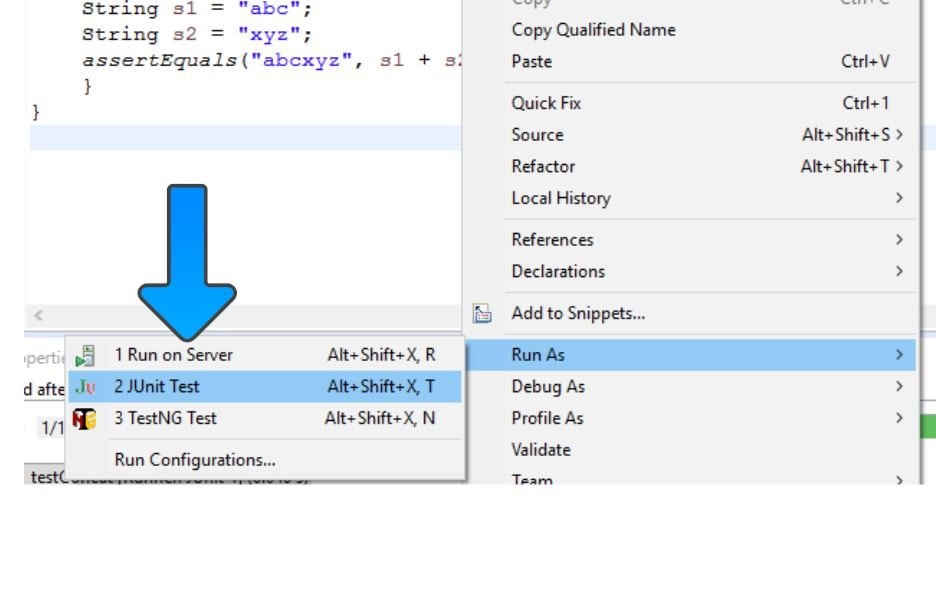
In the below example, we will see the order of JUnit annotations.
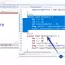
package com.testingdocs.junit;
import static org.junit.Assert.*;
import org.junit.After;
import org.junit.AfterClass;
import org.junit.Before;
import org.junit.BeforeClass;
import org.junit.Test;
/**
* A sample JUnit4 Test annotation demo
* class
*/
/**
* @author testingdocs
*
*/
public class SampleJUnit4TestCase {
/**
* @throws java.lang.Exception
*/
@BeforeClass
public static void setUpBeforeClass() throws Exception {
System.out.println("@BeforeClass");
}
/**
* @throws java.lang.Exception
*/
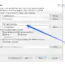
@AfterClass
public static void tearDownAfterClass() throws Exception {
System.out.println("@AfterClass");
}
/**
* @throws java.lang.Exception
*/
@Before
public void setUp() throws Exception {
System.out.println("@Before");
}
/**
* @throws java.lang.Exception
*/
@After
public void tearDown() throws Exception {
System.out.println("@After");
}
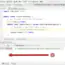
@Test
public void firstTestMethod() {
System.out.println("Test method 1");
fail("Not yet implemented1");
}
@Test
public void secondTestMethod() {
System.out.println("Test method 2");
fail("Not yet implemented2");
}
@Test
public void thridTestMethod() {
System.out.println("Test method 3");
fail("Not yet implemented3");
}
}
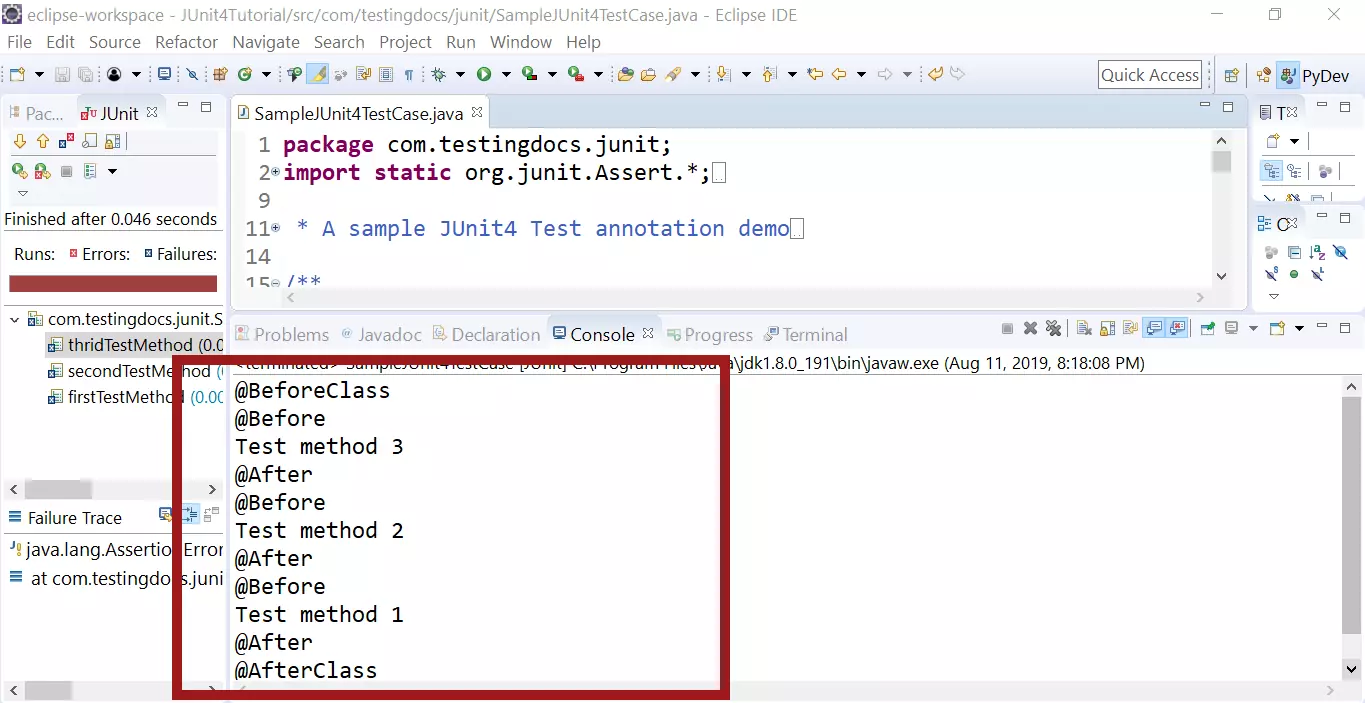
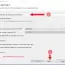
Run output
@BeforeClass
@Before
Test method 3
@After
@Before
Test method 2
@After
@Before
Test method 1
@After
@AfterClass