Calculator Java class
Calculator Java class
Let’s learn how to create a Calculator Java class with simple features like add, subtract, multiply, and divide methods. Later, we will learn how to test this class with the JUnit framework.
Things you need
- JDK install on your computer.
- IDE like Eclipse or IntelliJ.
(Note that you can also create a class using a source or text editor and
save it with a .java file extension. This approach has several drawbacks. You tend to know the disadvantages when you work with more than two classes.
So let’s use an IDE)
Steps to follow
Launch the IDE application on your machine.
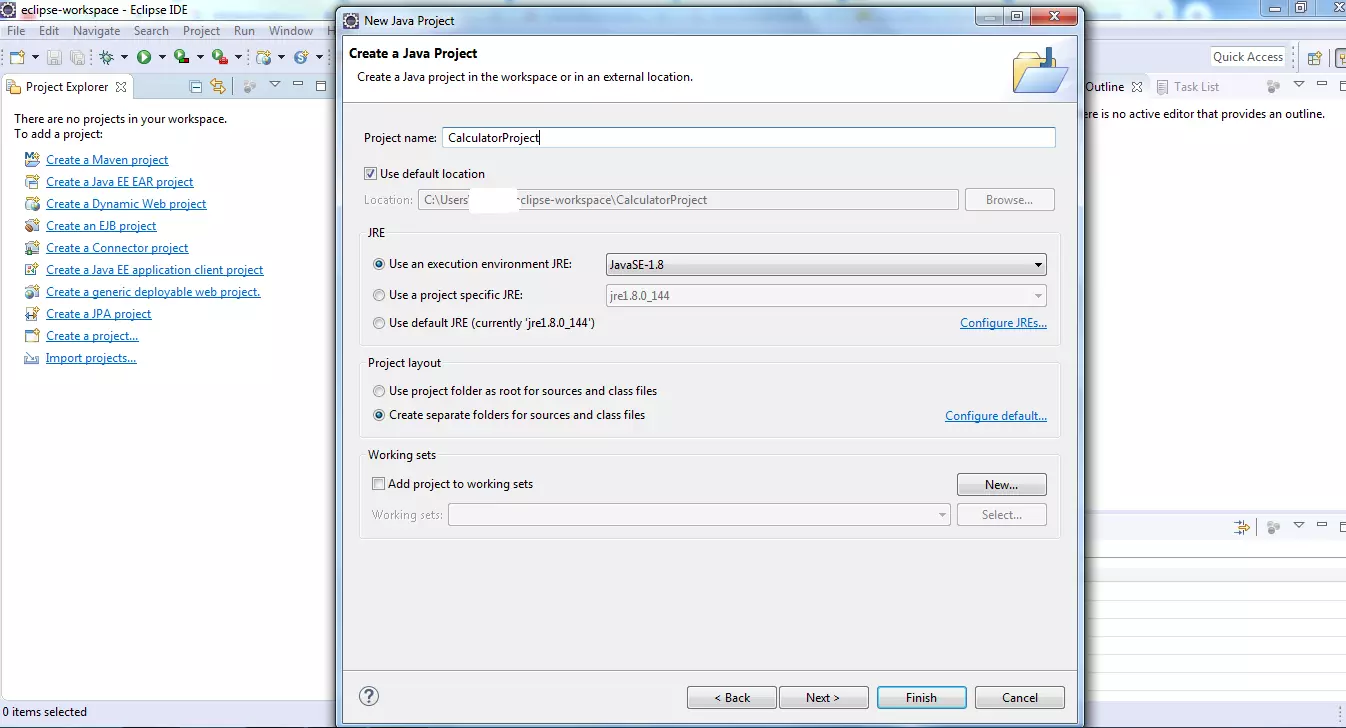
Create a Java Project
File >> New >> Project
For example, Calculator Project
Create a source package
For example: com.testingdocs.calculator
Create a class
Right-click on the src folder in the Project Explorer and choose the menu option:
New >> Java class
Create a Java class and name it Calculator. This class will contain the calculator methods.
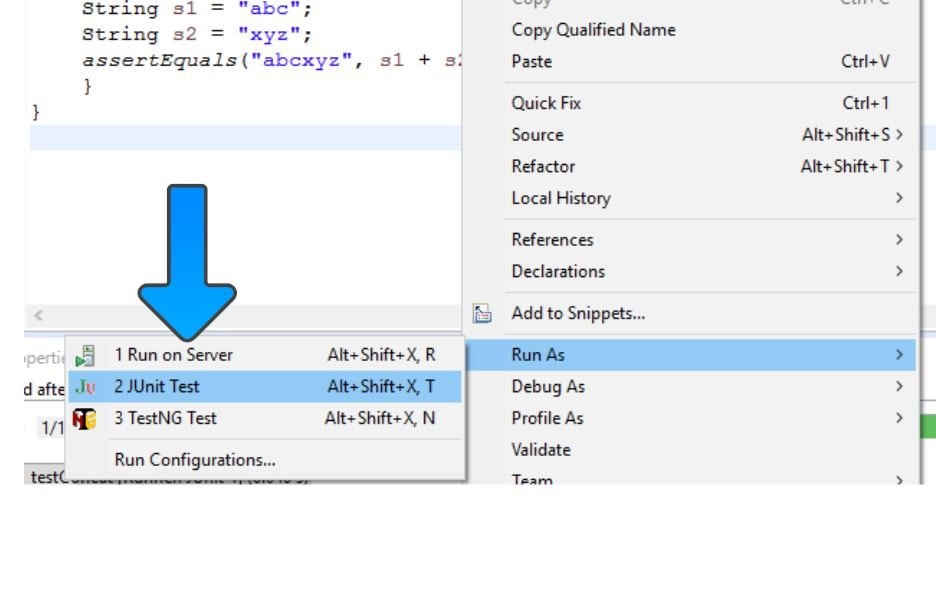
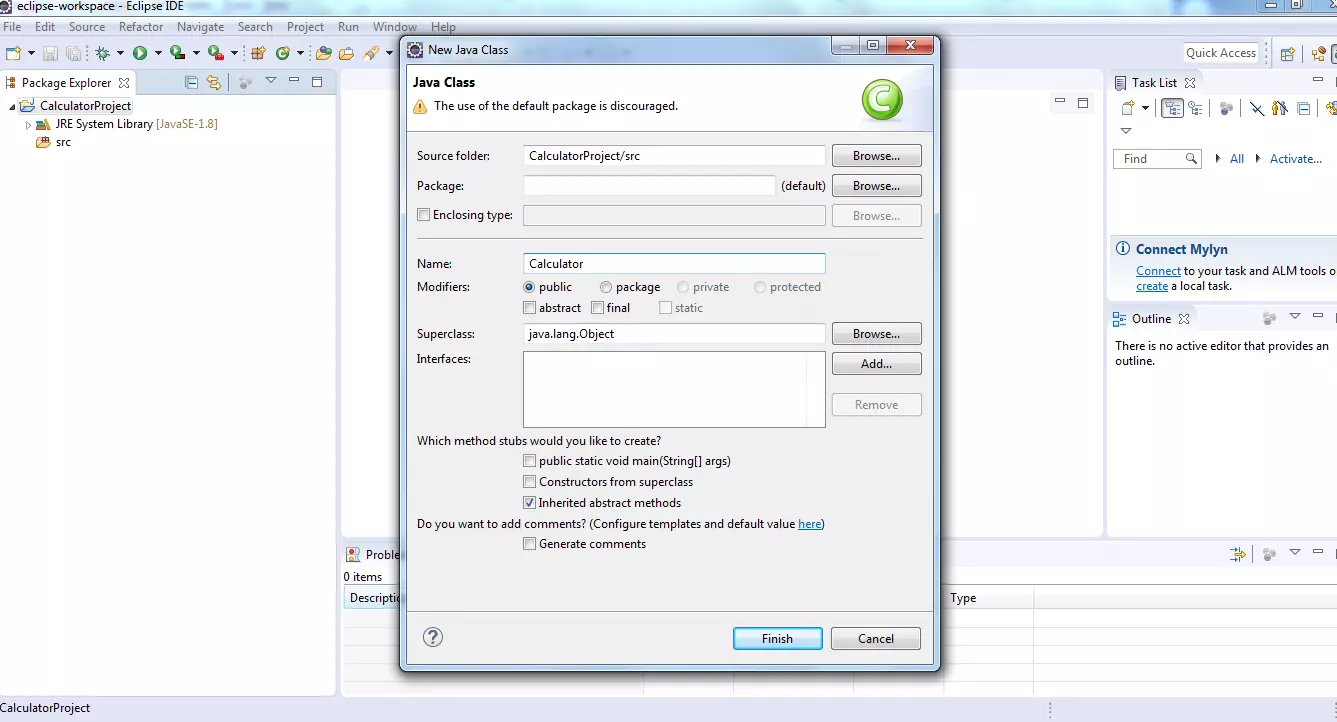
Eclipse
Screenshot in Eclipse IDE.
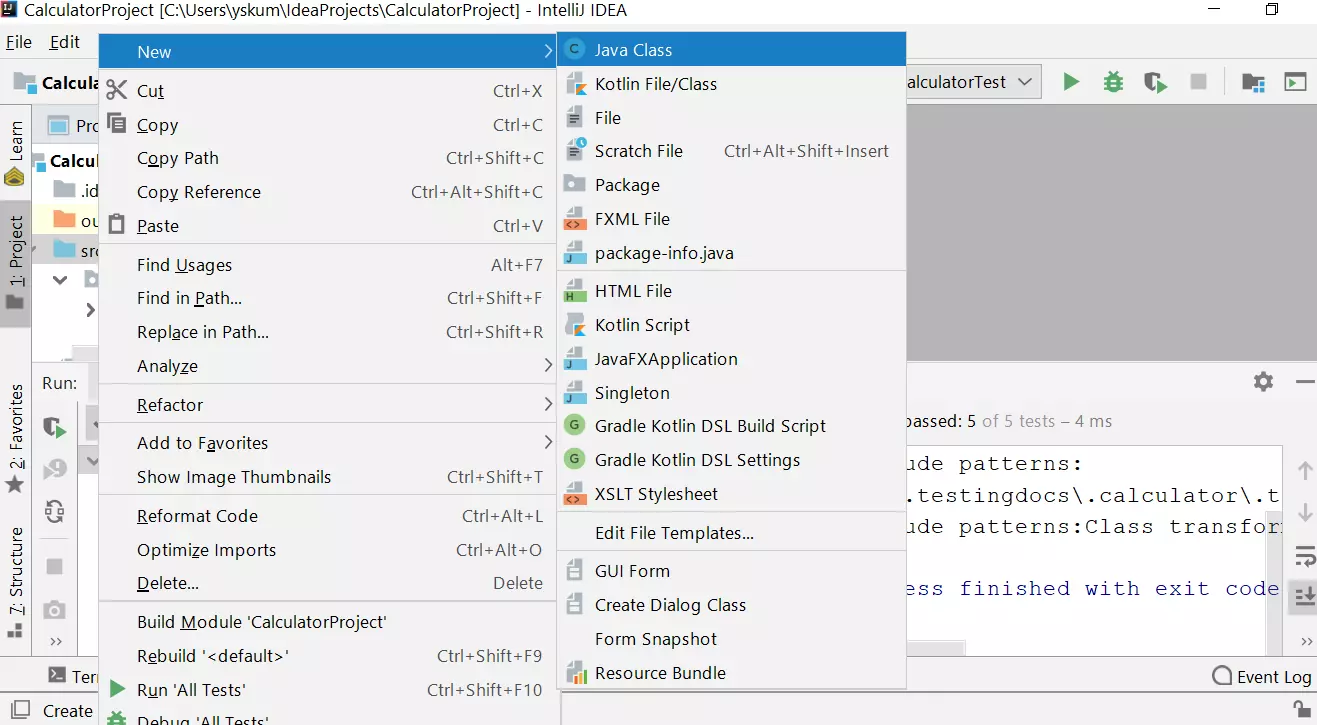
IntelliJ IDEA
Screenshot in IntelliJ IDEA IDE.
Calculator Java class
This class models some of the functions of a simple calculator which handles mathematical operations.
package com.testingdocs.calculator;
/**
* Calculator class:
* Basic Mathematical functions like
* Add,Subtract,Multiply,Divide.
*
*/
public class Calculator {
//no-arg constructor
public Calculator() {
}
/**
* Sum method.
*/
public int add(int a, int b) {
return a + b;
}
/**
* Subtract method.
*/
public int subtract(int a, int b) {
return a - b;
}
/**
* Multiply method.
*/
public long multiply(int a, int b) {
return a * b;
}
/**
* Divide method.
* Note that this method throws an exception when
* b is zero.
*/
public double divide(int a, int b) {
double result;
if (b == 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Divisor cannot divide by zero");
} else {
result = Double.valueOf(a)/Double.valueOf(b);
}
return result;
}
}

That’s it. The class simulates and provides the mathematical methods used in the calculator.
JUnit Tests for the Calculator class can be found here:
JUnit Tutorial on this website: