Create Symbolic Links in Linux
Overview
In this tutorial, we will learn how to create symbolic links in Linux. The ln command can be used to create both hard links and symbolic links.
A link in Linux is a pointer to a file. The pointer associates the filename with an inode number. There are two kinds of links:
- Hard Links
- Symbolic/Soft Links
Create a Symbolic link
To create a symbolic link to the file “sample.txt”, use
the following command:
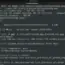
$ ln -s sample.txt symlink_name
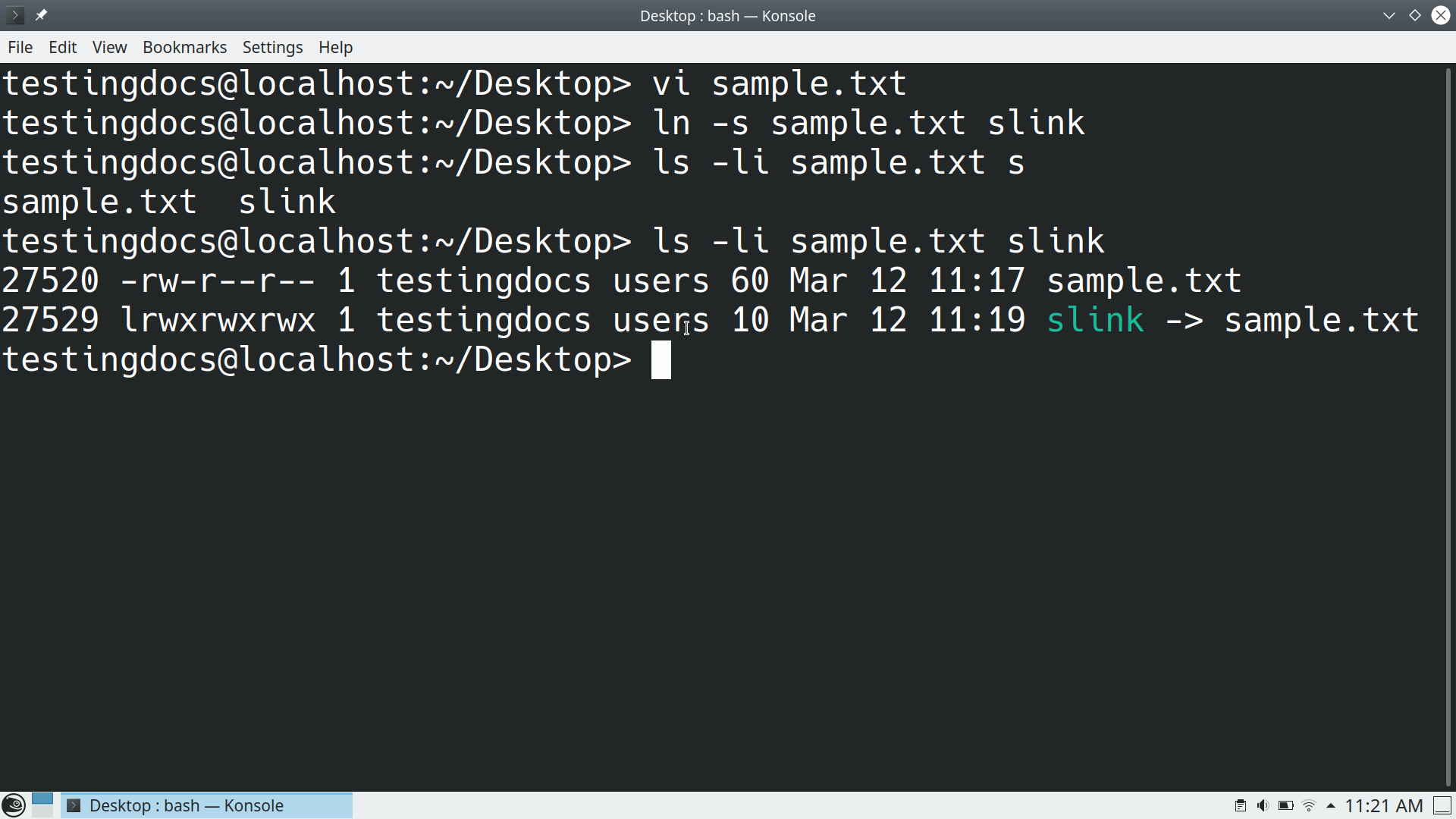
symlink_name is the symbolic link to the file. We can replace this with another name. In the example, we have created a symbolic link called ‘slink’ to the file ‘sample.txt’
Notice that the file and the symbolic link have different inode numbers.
We can also create a symbolic link to a directory on Linux. For example,
$ ln -s target_dir link_dir
That’s it.