C Identifiers
Overview
The name used to identify the variable,user-defined structure, function, etc in the C program is called Identifier. Identifiers abstract the actual memory addresses of the items to the programmer. The C compiler actually keeps track of the names and the actual physical memory address.
Naming Rules
In C language, we have some rules for identifier names.
- The first character of the identifier cannot be a digit. So, the name should start with a letter or an underscore character.
- The valid symbols are the uppercase letters [A-Z], the lowercase letters [a-z], the digits [0-9], and the special characters like underscore( _ ).
- The identifier cannot have white spaces.
- The name cannot be a C keyword or reserved word.
Note that C is a case-sensitive language. That means the C compiler distinguishes the upper and lower case letters even though the identifiers are spelled identically. For example, height and Height are two different identifiers.
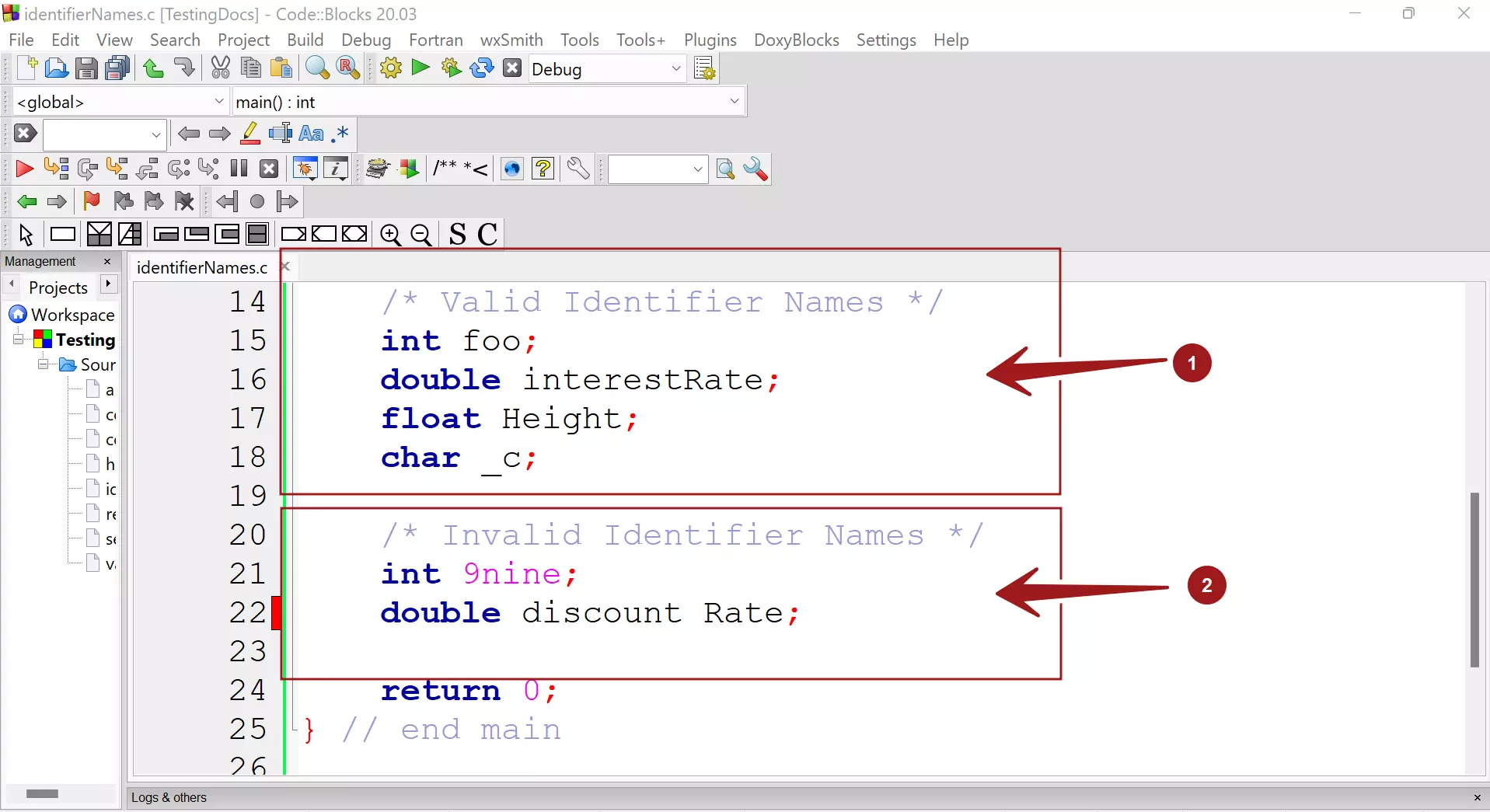
Examples
If the identifier name passes all the rules it’s called a legal or valid identifier. Names that disobey the rules are called invalid identifier names.
Some examples are as follows:
Exercise
Check if the following are valid identifiers in the C language:
student_Name
return
1_digit
retValue
counter
k
abc123
flight number