File Commands in Linux
Introduction
In this tutorial, we will see common File commands used in Linux while working with files. The most common operations are like viewing a file, editing a file, etc.
View a file
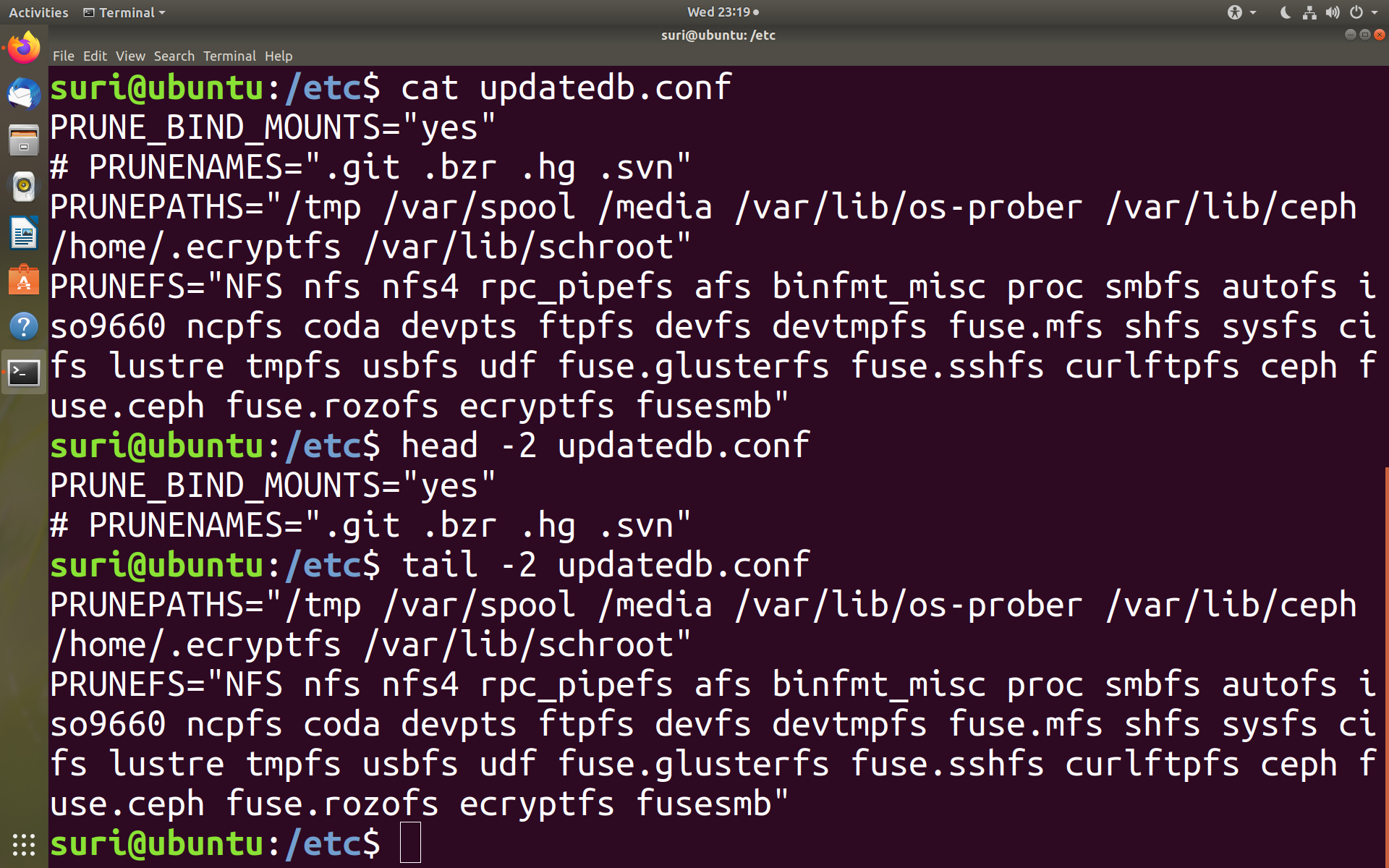
The basic command used to view a file in Linux is the cat command. It is mostly used for concatenating files and printing on the standard output. To know more about the cat command, use the below
$ man cat
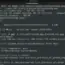
Let’s see an example of how to use the cat command to display a file to standard output. The format is the cat command followed by the filename to be displayed.
$ cat <filename>
$ cat updateddb.conf
The above command displays the file contents of the file updateddb.conf onto the terminal. Other useful commands are head and tail.
head
the head command displays the first lines to the file from the beginning as specified in the parameter.
The parameter specifies the number of lines to output.
tail
the tail command displays the last lines to the file from the bottom as specified in the parameter.
The parameter specifies the number of lines to output.
Example of using head and tail:
$ head -20 boot.log
$ tail -f server.log
These commands are useful while working with application servers. To view boot logs, and server logs.
The -f switch of the tail command is used to display the output as the file grows. For example log file of a server that is running.
To know more about the commands, we can use the man command.
$ man head
$ man tail
Create a File
We can use the touch command to create a file from the bash terminal. For example, to create a text file sample.txt, we can use the following command:
$ touch sample.txt
—
Linux Tutorials
Linux commands tutorial on this website:
https://www.testingdocs.com/linux-basic-commands-tutorial/
For more information on Ubuntu Linux, visit the website: