Flowgorithm Data Types [ 2024 ]
Flowgorithm Data Types
In this tutorial, we will learn about Flowgorithm Data Types. When we create or declare a variable in a Flowgorithm flowchart, we need to specify the variable’s data type.
Data Types Table
The Flowgorithm supports the following data types:
| Flowgorithm Data Type | Description |
| Integer | An Integer variable stores an integer number |
| Real | A Real variable stores a real number |
| String | A String variable stores a group of combinations of characters, numbers, and special symbols. |
| Boolean | Boolean variable stores either True or False |
| Array | An Array is a data structure. It can hold many values of the same data type. |
Integer
The Integer data type is the most commonly used. An integer variable is used to represent whole numbers. Whole numbers are numbers without fractions and are either positive or negative.
- An integer variable can store numbers 7, 40, 2018, etc.
- An integer variable cannot store numbers with fractions such as 40.5, 3.14, etc.
Example:
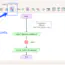
The number of students in a classroom is an integer datatype. The number represents a positive whole number or an empty classroom. We are sure we cannot have 40 and a half students in a class.
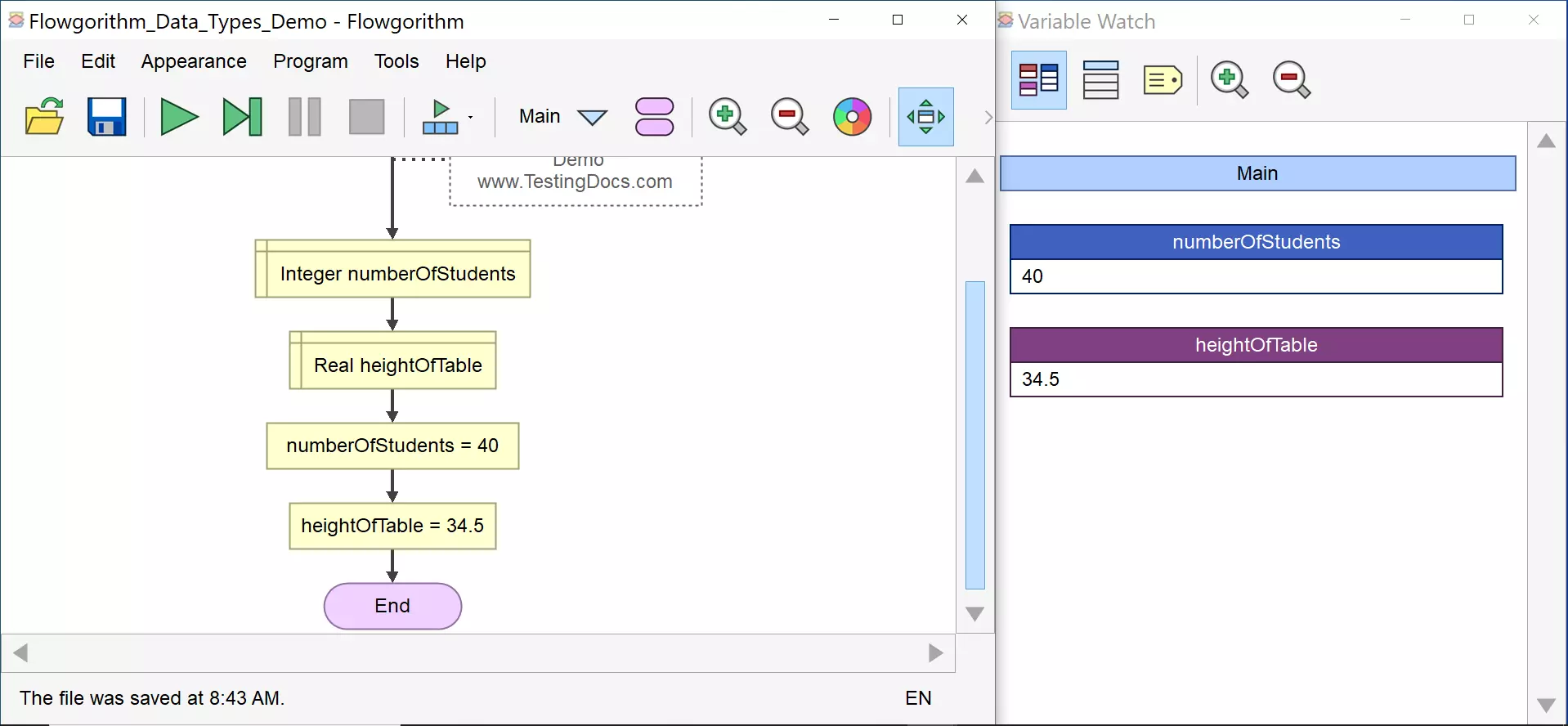
numberOfStudents = 40
The Variable Watch Window displays the integers in blue color.
Real
The Real data type represents numbers that can also have fractions. It can store both whole numbers and fractions, and the numbers can be either positive or negative.
They have the whole and fractional parts separated with a decimal. In programming languages like Java, this data type is float or double. (“double precision floating point”)
Example:
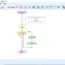
We use the Real data type to represent the table’s height. The height doesn’t always need to be in whole numbers. To represent a table height of 34.5 inches.
heightOfTable = 34.5
The Variable Watch Window displays the Real data type variables in purple.
String
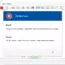
The String data type stores text, including words, letters, digits, etc. A pair of double quotes should surround the text. The Variable Watch Window displays the String data type variables in red.
Examples:
Examples include words, letters, digits, or anything else we might send with a text message.
- “Hello, World!“
- “C++ Programming for Beginners“
- “Albert Einstein“
- courseName like “CS100”
Boolean
The Boolean data type can only store “True” or “False” values. Boolean variables allow us to make decisions in the flowcharts. The Variable Watch Window displays the Boolean data type variables in gray-green color.
Example:
A real-world example of a Boolean data type that can hold only two values is a fan switch. The switch can be in only two states, either ON or OFF. The truth value of the Boolean expressions can either be true or false.
isSwitchOn = true
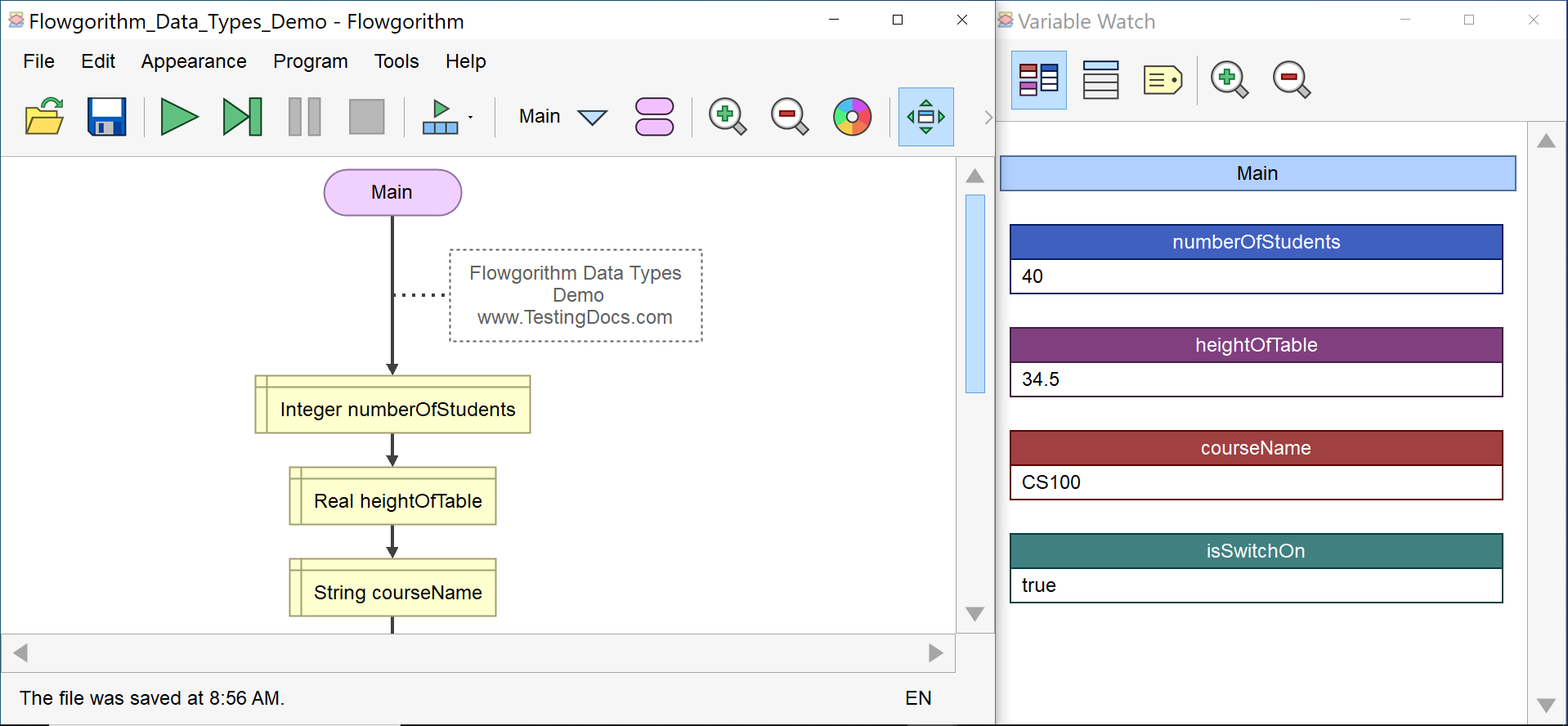
The Boolean data type is also called the Logical data type. The Boolean data type and the Boolean expression are the basis of decision-making in a flowchart. In the above example, the height of the table is 34.5 inches. The truth values for the expression can be much like Yes or No values:
Is the table height greater than 20 inches? -> Yes/ True
Is the table height greater than 40 inches? -> No/False
That’s it. This tutorial successfully taught us different algorithm data types. We will discuss Arrays in a separate tutorial.
Arrays
Arrays can hold many values of the same data type:
—
Flowgorithm Tutorials
Flowgorithm flowchart tutorials on this website:
Flowgorithm Website
For more information on the Flowgorithm tool, please visit the official website at