Java Data Types
Overview
Java data types are keywords used to allocate memory space for the data variables. A data type is used for representing the data in the RAM( Random-access Memory) of the computer.
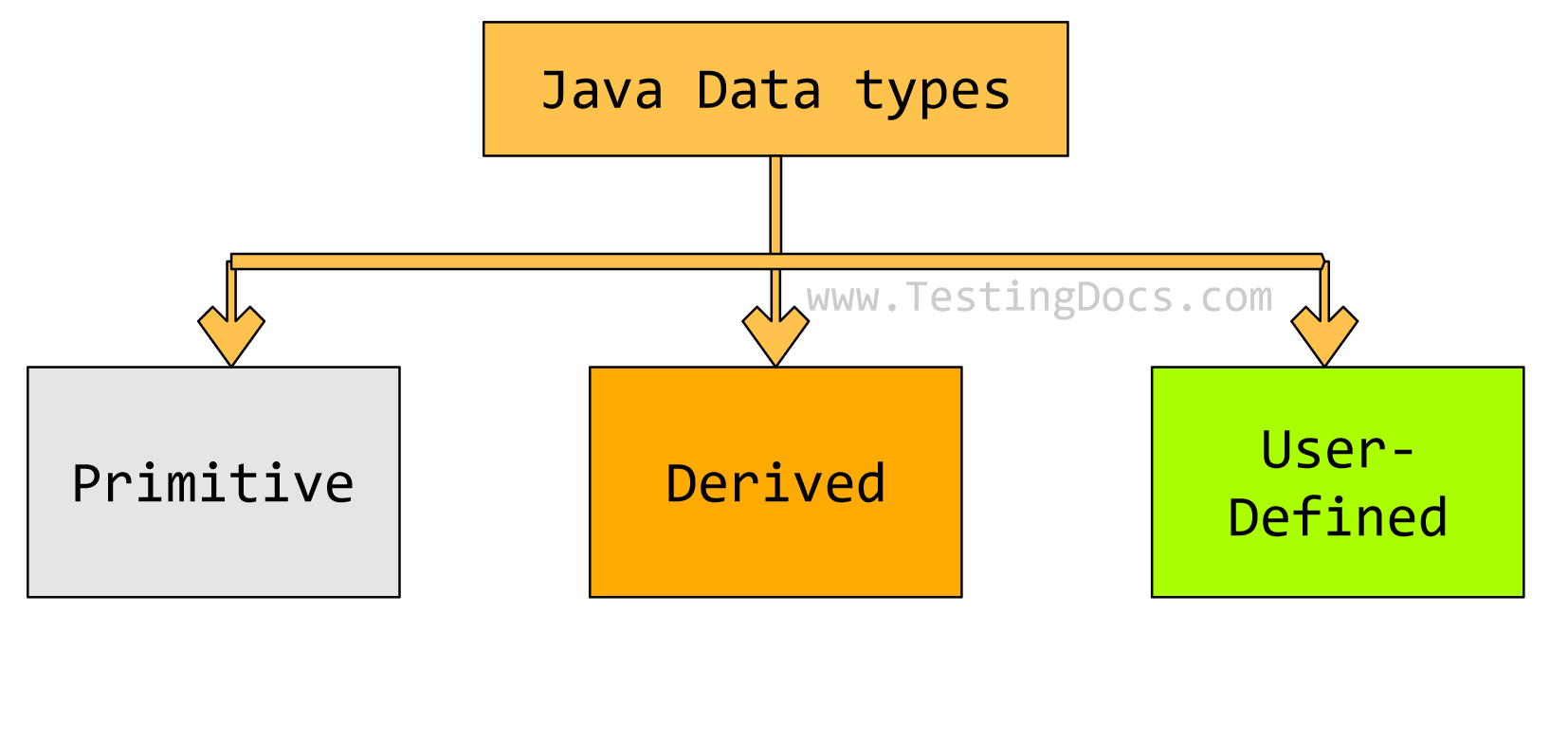
Data types in the Java programing language can be broadly classified into the following categories: primitive data types and non-primitive data types.
-
- Primitive data types
- Non-Primitive data types
- User-defined data types
Java is a statically typed language. The program variables must be declared before using them. We need to specify the variable’s data type and the variable name.
Primitive Data Types
Primitive data types are those whose variables allow us to store only one value at a time. Java is a strongly typed language. It means that every variable has a type. Java has eight primitive data types.
They can be further classified into the following categories:
Numeric Data types
- byte
- short
- int
- long
Floating point
- float
- double
Non-Numeric
- boolean
- char
Derived data types
Derived data types are those whose variables allow us to store multiple values of the same type. For example, an array. We cannot store values of different types.
User Defined Data Types
User-defined data types are defined by the programmers. Examples of user-defined data types:
- Class
- Interface
A programmer can define a class that has properties( instance variables). The instance variables can be of different dissimilar types.
—
Java Tutorials
Java Tutorial on this website:
https://www.testingdocs.com/java-tutorial/
For more information on Java, visit the official website :